The natively disordered loop of Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation-dependent conformational change and interacts with Pin1
- PMID: 23272207
- PMCID: PMC3525568
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052047
The natively disordered loop of Bcl-2 undergoes phosphorylation-dependent conformational change and interacts with Pin1
Abstract
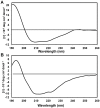
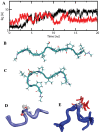
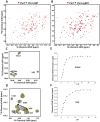
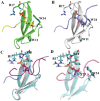
Bcl-2 plays a central role in the regulation of apoptosis. Structural studies of Bcl-2 revealed the presence of a flexible and natively disordered loop that bridges the Bcl-2 homology motifs, BH3 and BH4. This loop is phosphorylated on multiple sites in response to a variety of external stimuli, including the microtubule-targeting drugs, paclitaxel and colchicine. Currently, the underlying molecular mechanism of Bcl-2 phosphorylation and its biological significance remain elusive. In this study, we investigated the molecular characteristics of this anti-apoptotic protein. To this end, we generated synthetic peptides derived from the Bcl-2 loop, and multiple Bcl-2 loop truncation mutants that include the phosphorylation sites. Our results demonstrate that S87 in the flexible loop of Bcl-2 is the primary phosphorylation site for JNK and ERK2, suggesting some sequence or structural specificity for the phosphorylation by these kinases. Our NMR studies and molecular dynamics simulation studies support indicate that phosphorylation of S87 induces a conformational change in the peptide. Finally, we show that the phosphorylated peptides of the Bcl-2 loop can bind Pin1, further substantiating the phosphorylation-mediated conformation change of Bcl-2.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Microtubule-targeting drugs induce bcl-2 phosphorylation and association with Pin1.Neoplasia. 2001 Nov-Dec;3(6):550-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900213. Neoplasia. 2001. PMID: 11774038 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule-targeting drugs induce Bcl-2 phosphorylation and association with Pin1.Neoplasia. 2001 Jan-Feb;3(1):70-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.neo.7900131. Neoplasia. 2001. PMID: 11326318 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide binding induces large scale changes in inter-domain mobility in human Pin1.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jul 11;278(28):26174-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300796200. Epub 2003 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12686540
-
Exploring the molecular function of PIN1 by nuclear magnetic resonance.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2006 Jun;7(3):179-94. doi: 10.2174/138920306777452303. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2006. PMID: 16787258 Review.
-
Pin1 and nuclear receptors: a new language?J Cell Physiol. 2013 Sep;228(9):1799-801. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24316. J Cell Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23280577 Review.
Cited by
-
Domain-specific insight into the recognition of BH3-death motifs by the pro-survival Bcl-2 protein.Biophys J. 2022 Dec 6;121(23):4517-4525. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.10.041. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 36325615 Free PMC article.
-
JNK Signaling: Regulation and Functions Based on Complex Protein-Protein Partnerships.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016 Jul 27;80(3):793-835. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00043-14. Print 2016 Sep. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27466283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Solution NMR Spectroscopy in Target-Based Drug Discovery.Molecules. 2017 Aug 23;22(9):1399. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091399. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28832542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CK2 phosphorylation of human centrins 1 and 2 regulates their binding to the DNA repair protein XPC, the centrosomal protein Sfi1 and the phototransduction protein transducin β.FEBS Open Bio. 2014 Apr 24;4:407-19. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2014.04.002. eCollection 2014. FEBS Open Bio. 2014. PMID: 24918055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM (2003) The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene 22: 8590–8607. - PubMed
-
- Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 897–907. - PubMed
-
- Vander Heiden MG, Thompson CB (1999) Bcl-2 proteins: regulators of apoptosis or of mitochondrial homeostasis? Nat Cell Biol 1: E209–216. - PubMed
-
- Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407: 770–776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

