Inhibiting the interaction of cMET and IGF-1R with FAK effectively reduces growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23272972
- PMCID: PMC4052463
- DOI: 10.2174/1871520611313040009
Inhibiting the interaction of cMET and IGF-1R with FAK effectively reduces growth of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
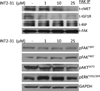
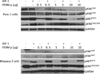
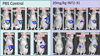
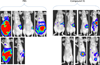
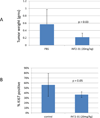
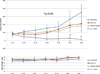
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal diseases with no effective treatment. Previously, we have shown that FAK is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and plays a key role in cancer cell survival and proliferation. FAK has been shown to interact with growth factor receptors including cMET and IGF-1R. As a novel therapeutic approach, we targeted the protein interaction of FAK with growth factor receptors to block tumor growth, alter signaling pathways and sensitize cells to chemotherapy. We have selected a small molecule compound (INT2-31) that decreases phosphorylation of AKT via disrupting interaction of FAK with cMET and IGF-1R. Our results demonstrate that interaction of a small molecule compound with FAK decreases phosphorylation of FAK Y397 while increasing FAK Y407 phosphorylation, without inhibiting the kinase activity of FAK and dramatically reduces downstream signaling to AKT. Our lead compound, INT2-31, demonstrates significant inhibition of tumor cell growth in two orthotopic models of pancreatic cancer. In addition, INT2-31 increases sensitivity to gemcitabine chemotherapy in a direct fresh biopsy xenograft model of pancreatic cancer growth.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A novel small molecule inhibitor of FAK and IGF-1R protein interactions decreases growth of human esophageal carcinoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Sep;11(7):629-37. doi: 10.2174/187152011796817718. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21707510
-
Disruption of the protein interaction between FAK and IGF-1R inhibits melanoma tumor growth.Cell Cycle. 2012 Sep 1;11(17):3250-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.21611. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22894899 Free PMC article.
-
FAK and IGF-IR interact to provide survival signals in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.Carcinogenesis. 2008 Jun;29(6):1096-107. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn026. Epub 2008 Feb 7. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18263593 Free PMC article.
-
Development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011 Sep;11(7):638-42. doi: 10.2174/187152011796817628. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21787276 Review.
-
Focal adhesion kinase-An emerging viable target in cancer and development of focal adhesion kinase inhibitors.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021 Mar;97(3):774-794. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13808. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2021. PMID: 33191630 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Extra-Cellular Matrix-Tumor Cell Crosstalk for Anti-Cancer Therapy: Emerging Alternatives to Integrin Inhibitors.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 22;10:1231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01231. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32793493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IFN-β is a potent inhibitor of insulin and insulin like growth factor stimulated proliferation and migration in human pancreatic cancer cells.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 May 15;5(6):2035-46. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26269762 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting FAK in human cancer: from finding to first clinical trials.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014 Jan 1;19(4):687-706. doi: 10.2741/4236. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2014. PMID: 24389213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in focal adhesion kinase (FAK)-targeting antitumor agents.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 20;15(26):20957-20984. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01880c. eCollection 2025 Jun 16. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40546697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation studies of novel F-18 labeled tumor imaging agents targeting focal adhesion kinase (FAK).RSC Adv. 2018 Mar 14;8(19):10333-10345. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00652k. eCollection 2018 Mar 13. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35540451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang GY, Wagner TD, Fuss M, Thomas CR., Jr Multimodality approaches for pancreatic cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(6):352–367. - PubMed
-
- Kircher SM, Krantz SB, Nimeiri HS, Mulcahy MF, Munshi HG, Benson AB., 3rd Therapy of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma: unresectable and borderline patients. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11(10):1555–1565. - PubMed
-
- Philip PA, Mooney M, Jaffe D, Eckhardt G, Moore M, Meropol N, Emens L, O'Reilly E, Korc M, Ellis L, Benedetti J, Rothenberg M, Willett C, Tempero M, Lowy A, Abbruzzese J, Simeone D, Hingorani S, Berlin J, Tepper J. Consensus report of the national cancer institute clinical trials planning meeting on pancreas cancer treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(33):5660–5669. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Korc M. Signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011;21(2):115–129. - PubMed
-
- Peters S, Adjei AA. MET: a promising anticancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2012;9(6):314–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

