Coilin displays differential affinity for specific RNAs in vivo and is linked to telomerase RNA biogenesis
- PMID: 23274112
- PMCID: PMC3568234
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.12.014
Coilin displays differential affinity for specific RNAs in vivo and is linked to telomerase RNA biogenesis
Abstract
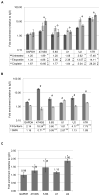
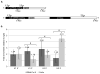
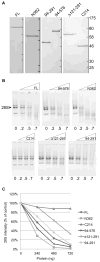
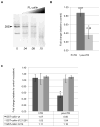
Coilin is widely known as the protein marker of the Cajal body, a subnuclear domain important to the biogenesis of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and telomerase, complexes that are crucial to pre-messenger RNA splicing and telomere maintenance, respectively. Extensive studies have characterized the interaction between coilin and the various other protein components of CBs and related subnuclear domains; however, only a few have examined interactions between coilin and nucleic acid. We have recently published that coilin is tightly associated with nucleic acid, displays RNase activity in vitro, and is redistributed to the ribosomal RNA (rRNA)-rich nucleoli in cells treated with the DNA-damaging agents cisplatin and etoposide. Here, we report a specific in vivo association between coilin and rRNA, U small nuclear RNA (snRNA), and human telomerase RNA, which is altered upon treatment with DNA-damaging agents. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation, we provide evidence of coilin interaction with specific regions of U snRNA gene loci. We have also utilized bacterially expressed coilin fragments in order to map the region(s) important for RNA binding and RNase activity in vitro. Additionally, we provide evidence of coilin involvement in the processing of human telomerase RNA both in vitro and in vivo.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Ramón y Cajal SR. Un sencillo metodo de coloracion selectiva del reticulo protoplasmico y sus efectos en los diversos organos nerviosos de vertebrados y invertebrados. Trab Lab Invest Biol (Madrid) 1903;2:129–221.
-
- Morris GE. The Cajal body. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1783:2108–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

