TGF-β1-containing exosomes from injured epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to initiate tissue regenerative responses and fibrosis
- PMID: 23274427
- PMCID: PMC3582210
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2012101031
TGF-β1-containing exosomes from injured epithelial cells activate fibroblasts to initiate tissue regenerative responses and fibrosis
Abstract
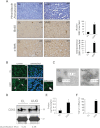
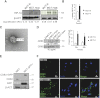
Hypoxia is associated with tissue injury and fibrosis but its functional role in fibroblast activation and tissue repair/regeneration is unknown. Using kidney injury as a model system, we demonstrate that injured epithelial cells produce an increased number of exosomes with defined genetic information to activate fibroblasts. Exosomes released by injured epithelial cells promote proliferation, α-smooth muscle actin expression, F-actin expression, and type I collagen production in fibroblasts. Fibroblast activation is dependent on exosomes delivering TGF-β1 mRNA among other yet to be identified moieties. This study suggests that TGF-β1 mRNA transported by exosomes constitutes a rapid response to initiate tissue repair/regenerative responses and activation of fibroblasts when resident parenchyma is injured. The results also inform potential utility of exosome-targeted therapies to control tissue fibrosis.
Figures


Comment in
-
A new look at tubulointerstitial communication with exosomes.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Feb;24(3):330-2. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013010052. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23393322 No abstract available.
References
-
- Tomasek JJ, Gabbiani G, Hinz B, Chaponnier C, Brown RA: Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 349–363, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Kalluri R: Cellular and molecular pathways that lead to progression and regression of renal fibrogenesis. Curr Mol Med 5: 467–474, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Coresh J, Astor BC, Greene T, Eknoyan G, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease and decreased kidney function in the adult US population: Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Kidney Dis 41: 1–12, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 CA151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 055001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024148/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK081576/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007760/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA-151925/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-155370/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 2T32DK007760-11/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA125550/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

