Epigenetic regulation of adipogenesis by PHF2 histone demethylase
- PMID: 23274892
- PMCID: PMC3636657
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0628
Epigenetic regulation of adipogenesis by PHF2 histone demethylase
Abstract
PHF2 is a JmjC family histone demethylase that removes the methyl group from H3K9me2 and works as a coactivator for several metabolism-related transcription factors. In this study, we examined the in vivo role of PHF2 in mice. We generated Phf2 floxed mice, systemic Phf2 null mice by crossing Phf2 floxed mice with CMV-Cre transgenic mice, and tamoxifen-inducible Phf2 knockout mice by crossing Phf2 floxed mice with Cre-ERT2 transgenic mice. Systemic Phf2 null mice had partial neonatal death and growth retardation and exhibited less adipose tissue and reduced adipocyte numbers compared with control littermates. Tamoxifen-induced conditional knockout of PHF2 resulted in impaired adipogenesis in stromal vascular cells from the adipose tissue of tamoxifen-inducible Phf2 knockout mice as well as of Phf2 knocked-down 3T3-L1 cells. PHF2 interacts with CEBPA and demethylates H3K9me2 in the promoters of CEBPA-regulated adipogenic genes. These findings suggest that PHF2 histone demethylase potentiates adipogenesis through interaction with CEBPA in vivo. Taken together, PHF2 may be a novel therapeutic target in the treatment of obesity and the metabolic syndrome.
Figures

 , the LoxP sites;
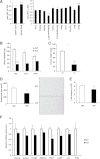
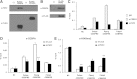
, the LoxP sites;  , Frt sites. B: Southern blotting analysis of targeted embryonic stem cell clones. Restriction enzymes used for screening recombination events with probe A were BglII and HindIII. An 8.3-kb fragment in WT and a 5.3-kb fragment after homologous recombination were expected with probe A. Restriction enzymes used for screening recombination events with probe B were EcoRI and NsiI. A 9.0-kb fragment in WT and a 7.2-kb fragment after homologous recombination were expected with probe B. C: To detect the presence of the LacZ allele (Z) and the WT allele (+), primers P1, P2, and P3 were used. The PCR bands of the WT allele (242 bp) and the LacZ allele (495 bp) are indicated. D: To detect the presence of the floxed allele (fl) and the WT allele (+), primers P4 and P5 were used. The PCR bands of the WT allele (162 bp) and the floxed allele (245 bp) are indicated. E: Western blot analysis of PHF2 protein expression in Phf2Z/Z mice. Extracts of mouse embryonic fibroblasts from WT or Phf2Z/Z were immunoprecipitated and detected with anti-PHF2 antibody. WT, wild type.
, Frt sites. B: Southern blotting analysis of targeted embryonic stem cell clones. Restriction enzymes used for screening recombination events with probe A were BglII and HindIII. An 8.3-kb fragment in WT and a 5.3-kb fragment after homologous recombination were expected with probe A. Restriction enzymes used for screening recombination events with probe B were EcoRI and NsiI. A 9.0-kb fragment in WT and a 7.2-kb fragment after homologous recombination were expected with probe B. C: To detect the presence of the LacZ allele (Z) and the WT allele (+), primers P1, P2, and P3 were used. The PCR bands of the WT allele (242 bp) and the LacZ allele (495 bp) are indicated. D: To detect the presence of the floxed allele (fl) and the WT allele (+), primers P4 and P5 were used. The PCR bands of the WT allele (162 bp) and the floxed allele (245 bp) are indicated. E: Western blot analysis of PHF2 protein expression in Phf2Z/Z mice. Extracts of mouse embryonic fibroblasts from WT or Phf2Z/Z were immunoprecipitated and detected with anti-PHF2 antibody. WT, wild type.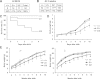

References
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science 2001;293:1074–1080 - PubMed
-
- Klose RJ, Kallin EM, Zhang Y. JmjC-domain-containing proteins and histone demethylation. Nat Rev Genet 2006;7:715–727 - PubMed
-
- Shi Y. Histone lysine demethylases: emerging roles in development, physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet 2007;8:829–833 - PubMed
-
- Agger K, Christensen J, Cloos PA, Helin K. The emerging functions of histone demethylases. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2008;18:159–168 - PubMed
-
- Baba A, Ohtake F, Okuno Y, et al. PKA-dependent regulation of the histone lysine demethylase complex PHF2-ARID5B. Nat Cell Biol 2011;13:668–675 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

