EphA5-EphrinA5 interactions within the ventromedial hypothalamus influence counterregulatory hormone release and local glutamine/glutamate balance during hypoglycemia
- PMID: 23274893
- PMCID: PMC3609598
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0982
EphA5-EphrinA5 interactions within the ventromedial hypothalamus influence counterregulatory hormone release and local glutamine/glutamate balance during hypoglycemia
Abstract
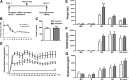
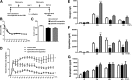
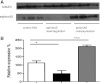
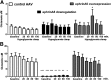
Activation of β-cell EphA5 receptors by its ligand ephrinA5 from adjacent β-cells has been reported to decrease insulin secretion during hypoglycemia. Given the similarities between islet and ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) glucose sensing, we tested the hypothesis that the EphA5/ephrinA5 system might function within the VMH during hypoglycemia to stimulate counterregulatory hormone release as well. Counterregulatory responses and glutamine/glutamate concentrations in the VMH were assessed during a hyperinsulinemic-hypoglycemic glucose clamp study in chronically catheterized awake male Sprague-Dawley rats that received an acute VMH microinjection of ephrinA5-Fc, chronic VMH knockdown, or overexpression of ephrinA5 using an adenoassociated viral construct. Local stimulation of VMH EphA5 receptors by ephrinA5-Fc or ephrinA5 overexpression increased, whereas knockdown of VMH ephrinA5 reduced counterregulatory responses during hypoglycemia. Overexpression of VMH ephrinA5 transiently increased local glutamate concentrations, whereas ephrinA5 knockdown produced profound suppression of VMH interstitial fluid glutamine concentrations in the basal state and during hypoglycemia. Changes in ephrinA5/EphA5 interactions within the VMH, a key brain glucose-sensing region, act in concert with islets to restore glucose homeostasis during acute hypoglycemia, and its effect on counterregulation may be mediated by changes in glutamate/glutamine cycling.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hypothalamic EphA5 facilitates counterregulatory responses: possible role for bidirectional signaling leading to bistability that enhances responsiveness to hypoglycemia.Diabetes. 2013 Apr;62(4):1014-6. doi: 10.2337/db12-1735. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23520275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977–986 - PubMed
-
- UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837–853 - PubMed
-
- Amiel SA, Tamborlane WV, Simonson DC, Sherwin RS. Defective glucose counterregulation after strict glycemic control of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1987;316:1376–1383 - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE. Glucose counterregulation in man. Diabetes 1981;30:261–264 - PubMed
-
- Saccà L, Cryer PE, Sherwin RS. Blood glucose regulates the effects of insulin and counterregulatory hormones on glucose production in vivo. Diabetes 1979;28:533–536 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

