Rac1 is a novel regulator of contraction-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 23274900
- PMCID: PMC3609592
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-0491
Rac1 is a novel regulator of contraction-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle
Abstract
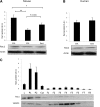
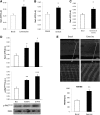
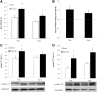
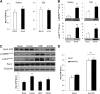
In skeletal muscle, the actin cytoskeleton-regulating GTPase, Rac1, is necessary for insulin-dependent GLUT4 translocation. Muscle contraction increases glucose transport and represents an alternative signaling pathway to insulin. Whether Rac1 is activated by muscle contraction and regulates contraction-induced glucose uptake is unknown. Therefore, we studied the effects of in vivo exercise and ex vivo muscle contractions on Rac1 signaling and its regulatory role in glucose uptake in mice and humans. Muscle Rac1-GTP binding was increased after exercise in mice (~60-100%) and humans (~40%), and this activation was AMP-activated protein kinase independent. Rac1 inhibition reduced contraction-stimulated glucose uptake in mouse muscle by 55% in soleus and by 20-58% in extensor digitorum longus (EDL; P < 0.01). In agreement, the contraction-stimulated increment in glucose uptake was decreased by 27% (P = 0.1) and 40% (P < 0.05) in soleus and EDL muscles, respectively, of muscle-specific inducible Rac1 knockout mice. Furthermore, depolymerization of the actin cytoskeleton decreased contraction-stimulated glucose uptake by 100% and 62% (P < 0.01) in soleus and EDL muscles, respectively. These are the first data to show that Rac1 is activated during muscle contraction in murine and human skeletal muscle and suggest that Rac1 and possibly the actin cytoskeleton are novel regulators of contraction-stimulated glucose uptake.
Figures
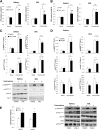
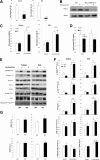
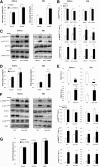
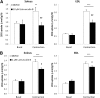
Comment in
-
ContRac1ion-mediated glucose uptake: a central role for Rac1.Diabetes. 2013 Apr;62(4):1024-5. doi: 10.2337/db12-1789. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23520279 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Goldstein MS, Mullick V, Huddlestun B, Levine R. Action of muscular work on transfer of sugars across cell barriers; comparison with action of insulin. Am J Physiol 1953;173:212–216 - PubMed
-
- Holloszy JO, Narahara HT. Studies of tissue permeability. X. Changes in permeability to 3-methylglucose associated with contraction of isolated frog muscle. J Biol Chem 1965;240:3493–3500 - PubMed
-
- Rose AJ, Richter EA. Skeletal muscle glucose uptake during exercise: how is it regulated? Physiology (Bethesda) 2005;20:260–270 - PubMed
-
- Lauritzen HP, Reynet C, Schjerling P, et al. Gene gun bombardment-mediated expression and translocation of EGFP-tagged GLUT4 in skeletal muscle fibres in vivo. Pflugers Arch 2002;444:710–721 - PubMed
-
- Klip A, Ramlal T, Young DA, Holloszy JO. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett 1987;224:224–230 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

