Permanent neonatal diabetes in INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs
- PMID: 23274907
- PMCID: PMC3636654
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-1065
Permanent neonatal diabetes in INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs
Abstract
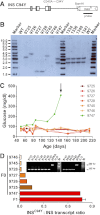
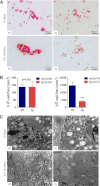
Mutations in the insulin (INS) gene may cause permanent neonatal diabetes mellitus (PNDM). Ins2 mutant mouse models provided important insights into the disease mechanisms of PNDM but have limitations for translational research. To establish a large animal model of PNDM, we generated INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs. A line expressing high levels of INS(C94Y) mRNA (70-86% of wild-type INS transcripts) exhibited elevated blood glucose soon after birth but unaltered β-cell mass at the age of 8 days. At 4.5 months, INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs exhibited 41% reduced body weight, 72% decreased β-cell mass (-53% relative to body weight), and 60% lower fasting insulin levels compared with littermate controls. β-cells of INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs showed a marked reduction of insulin secretory granules and severe dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cataract development was already visible in 8-day-old INS(C94Y) transgenic pigs and became more severe with increasing age. Diabetes-associated pathological alterations of kidney and nervous tissue were not detected during the observation period of 1 year. The stable diabetic phenotype and its rescue by insulin treatment make the INS(C94Y) transgenic pig an attractive model for insulin supplementation and islet transplantation trials, and for studying developmental consequences of maternal diabetes mellitus.
Figures


References
-
- Yoshioka M, Kayo T, Ikeda T, Koizumi A. A novel locus, Mody4, distal to D7Mit189 on chromosome 7 determines early-onset NIDDM in nonobese C57BL/6 (Akita) mutant mice. Diabetes 1997;46:887–894 - PubMed
-
- Herbach N, Rathkolb B, Kemter E, et al. Dominant-negative effects of a novel mutated Ins2 allele causes early-onset diabetes and severe beta-cell loss in Munich Ins2C95S mutant mice. Diabetes 2007;56:1268–1276 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

