Evolutionary inference via the Poisson Indel Process
- PMID: 23275296
- PMCID: PMC3557041
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1220450110
Evolutionary inference via the Poisson Indel Process
Abstract
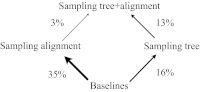
We address the problem of the joint statistical inference of phylogenetic trees and multiple sequence alignments from unaligned molecular sequences. This problem is generally formulated in terms of string-valued evolutionary processes along the branches of a phylogenetic tree. The classic evolutionary process, the TKF91 model [Thorne JL, Kishino H, Felsenstein J (1991) J Mol Evol 33(2):114-124] is a continuous-time Markov chain model composed of insertion, deletion, and substitution events. Unfortunately, this model gives rise to an intractable computational problem: The computation of the marginal likelihood under the TKF91 model is exponential in the number of taxa. In this work, we present a stochastic process, the Poisson Indel Process (PIP), in which the complexity of this computation is reduced to linear. The Poisson Indel Process is closely related to the TKF91 model, differing only in its treatment of insertions, but it has a global characterization as a Poisson process on the phylogeny. Standard results for Poisson processes allow key computations to be decoupled, which yields the favorable computational profile of inference under the PIP model. We present illustrative experiments in which Bayesian inference under the PIP model is compared with separate inference of phylogenies and alignments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
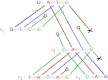
 and root Ω, where each string is subject to insertion, deletion, and substitution processes. Stars denote nucleotide insertion events, crosses denote deletion events, and circles denote substitution events.
and root Ω, where each string is subject to insertion, deletion, and substitution processes. Stars denote nucleotide insertion events, crosses denote deletion events, and circles denote substitution events.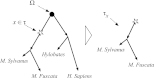
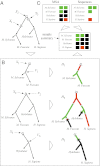
References
-
- Thorne JL, Kishino H, Felsenstein J. An evolutionary model for maximum likelihood alignment of DNA sequences. J Mol Evol. 1991;33(2):114–124. - PubMed
-
- Holmes I, Bruno WJ. Evolutionary HMMs: A Bayesian approach to multiple alignment. Bioinformatics. 2001;17(9):803–820. - PubMed
-
- Hein J. An algorithm for statistical alignment of sequences related by a binary tree. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2001;6:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Steel M, Hein J. Applying the Thorne-Kishino-Felsenstein model to sequence evolution on a star-shaped tree. Appl Math Lett. 2001;14(6):679–684.
-
- Metzler D, Fleissner R, Wakolbinger A, von Haeseler A. Assessing variability by joint sampling of alignments and mutation rates. J Mol Evol. 2001;53(6):660–669. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

