Astrocytes revisited: concise historic outlook on glutamate homeostasis and signaling
- PMID: 23275317
- PMCID: PMC3541578
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2012.53.518
Astrocytes revisited: concise historic outlook on glutamate homeostasis and signaling
Abstract
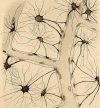
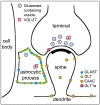
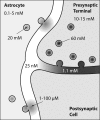
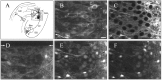
Astroglia is a main type of brain neuroglia, which includes many cell sub-types that differ in their morphology and physiological properties and yet are united by the main function, which is the maintenance of brain homeostasis. Astrocytes employ a variety of mechanisms for communicating with neuronal networks. The communication mediated by neurotransmitter glutamate has received a particular attention. Glutamate is de novo synthesized exclusively in astrocytes; astroglia-derived glutamine is the source of glutamate for neurons. Glutamate is released from both neurons and astroglia through exocytosis, although various other mechanisms may also play a role. Glutamate-activated specific receptors trigger excitatory responses in neurons and astroglia. Here we overview main properties of glutamatergic transmission in neuronal-glial networks and identify some future challenges facing the field.
Figures

References
-
- Virchow R. Cellular pathology: as based upon physiological and pathological histology. Twenty lectures delivered in the pathological institute of Berlin during the months of February, March and April, 1858 [in German]. First edition ed. Berlin: August Hirschwald; 1858.
-
- Golgi C. On structure of the gray matter of the brain. Gazzetta Medica Italiana Lombardia. 1873;33:244–6. [in Italian]
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

