Role of the vagus in the reduced pancreatic exocrine function in copper-deficient rats
- PMID: 23275611
- PMCID: PMC6842873
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00402.2012
Role of the vagus in the reduced pancreatic exocrine function in copper-deficient rats
Abstract
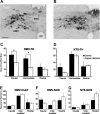
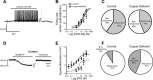
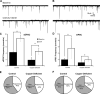
Copper plays an essential role in the function and development of the central nervous system and exocrine pancreas. Dietary copper limitation is known to result in noninflammatory atrophy of pancreatic acinar tissue. Our recent studies have suggested that vagal motoneurons regulate pancreatic exocrine secretion (PES) by activating selective subpopulations of neurons within vagovagal reflexive neurocircuits. We used a combination of in vivo, in vitro, and immunohistochemistry techniques in a rat model of copper deficiency to investigate the effects of a copper-deficient diet on the neural pathways controlling PES. Duodenal infusions of Ensure or casein, as well as microinjections of sulfated CCK-8, into the dorsal vagal complex resulted in an attenuated stimulation of PES in copper-deficient animals compared with controls. Immunohistochemistry of brain stem slices revealed that copper deficiency reduced the number of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive, but not neuronal nitric oxide synthase- or choline acetyltransferase-immunoreactive, neurons in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV). Moreover, a copper-deficient diet reduced the number of large (>11 neurons), but not small, intrapancreatic ganglia. Electrophysiological recordings showed that DMV neurons from copper-deficient rats are less responsive to CCK-8 or pancreatic polypeptide than are DMV neurons from control rats. Our results demonstrate that copper deficiency decreases efferent vagal outflow to the exocrine pancreas. These data indicate that the combined selective loss of acinar pancreatic tissue and the decreased excitability of efferent vagal neurons induce a deficit in the vagal modulation of PES.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cholecystokinin-8s excites identified rat pancreatic-projecting vagal motoneurons.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):G484-92. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00116.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17569742
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 excites pancreas-projecting preganglionic vagal motoneurons.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Jun;292(6):G1474-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00562.2006. Epub 2007 Feb 22. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17322063
-
Vagally mediated, nonparacrine effects of cholecystokinin-8s on rat pancreatic exocrine secretion.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Aug;293(2):G493-500. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00118.2007. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17569741
-
The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and regulation of pancreatic secretory function.Exp Physiol. 2013 Jan;98(1):25-37. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2012.066472. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Exp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 22660814 Review.
-
Secretion from acinar cells of the exocrine pancreas: role of enteropancreatic reflexes and cholecystokinin.Cell Biol Int. 2009 Jan;33(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellbi.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Oct 7. Cell Biol Int. 2009. PMID: 18948215 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute pancreatitis decreases the sensitivity of pancreas-projecting dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurones to group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists in rats.J Physiol. 2014 Mar 15;592(6):1411-21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.270108. Epub 2014 Jan 20. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24445314 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced Pancreatic Exocrine Function and Organellar Disarray in a Canine Model of Acute Pancreatitis.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 19;11(2):e0148458. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148458. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26895040 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of the nervous system in pancreatic cancer.Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2021 Mar 29;5(5):623-633. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12459. eCollection 2021 Sep. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2021. PMID: 34585047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural plasticity in pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Nov;12(11):649-59. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2015.166. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26460352 Review.
-
Role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the regulation of pancreatic functions.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 15;87(4):535-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24355565 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahren B , Gingerich RL , Havel PJ. Effects of cholecystokinin and glucagon-like peptide 1 on the secretion of pancreatic polypeptide in mice. Regul Pept 59: 297– 302, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR , Fox EA , Powley TL. Localization of vagal preganglionics that stimulate insulin and glucagon secretion. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 258: R160– R168, 1990. - PubMed
-
- Berthoud HR , Powley TL. Characteristics of gastric and pancreatic responses to vagal stimulation with varied frequencies: evidence for different fiber calibers? J Auton Nerv Syst 19: 77– 84, 1987. - PubMed
-
- Browning KN , Coleman FH , Travagli RA. Characterization of pancreas-projecting rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurons. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G950– G955, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

