Intravitreal ranibizumab and laser photocoagulation in the management of idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia type 1: a case report
- PMID: 23275792
- PMCID: PMC3530150
- DOI: 10.1159/000342848
Intravitreal ranibizumab and laser photocoagulation in the management of idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia type 1: a case report
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia (IJRT) type 1 represents an uncommon cause of congenital unilateral visual loss and it typically affects males. Decrease in visual acuity is caused by serous and lipid exudation into the fovea with cystoid macular edema. In some cases, spontaneous resolution may be observed, but when there is a progressive loss of visual acuity, laser photocoagulation is often necessary. This treatment is not always successful and therapy for this condition is still controversial.
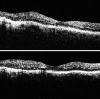
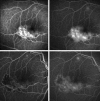
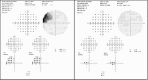
Case presentation: A 57-year-old man referred a 2-month history of blurred and distorted vision in the right eye. Best-corrected visual acuity was 20/50 in the right eye and 20/20 in the left eye. Fundus examination showed temporal macular edema, confirmed by optical coherence tomography. Fluorescein angiography showed a localized area of hyperfluorescence probably due to telangiectasia type 1 located below the inferior temporal area of the fovea. A combined therapy of intravitreal ranibizumab injection and laser photocoagulation was performed. Visual acuity improved from 20/50 to 20/32 and the therapy was well tolerated by the patient. After 3 years of follow-up, both visual acuity and fundus examination were stable.
Conclusions: This case suggests that the combined use of ranibizumab and laser photocoagulation may be considered an effective treatment for JRT type 1, leading to an improvement in both visual acuity and macular edema. We believe that intravitreal ranibizumab injection associated with laser photocoagulation should be considered as treatment for IJRT type 1.
Keywords: Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia; Intravitreal injection; Laser photocoagulation; Ranibizumab.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined treatment with intravitreal bevacizumab and laser photocoagulation for exudative maculopathy in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.Ophthalmic Genet. 2017 Sep-Oct;38(5):490-493. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2017.1279183. Epub 2017 Jan 25. Ophthalmic Genet. 2017. PMID: 28121209
-
COMBINATION THERAPY OF INTRAVITREAL RANIBIZUMAB AND SUBTHRESHOLD MICROPULSE PHOTOCOAGULATION FOR MACULAR EDEMA SECONDARY TO BRANCH RETINAL VEIN OCCLUSION: 6-MONTH RESULT.Retina. 2019 Jul;39(7):1377-1384. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000002165. Retina. 2019. PMID: 29689025 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia.Optometry. 2008 Nov;79(11):653-62. doi: 10.1016/j.optm.2008.04.099. Optometry. 2008. PMID: 19811762
-
Practical Lessons from Protocol I for the Management of Diabetic Macular Edema.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;60:91-108. doi: 10.1159/000459692. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28427069 Review.
-
Intravitreal Ranibizumab in Diabetic Macular Edema: Long-Term Outcomes.Dev Ophthalmol. 2017;60:63-70. doi: 10.1159/000460496. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Dev Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28427066 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparison of anatomical and visual outcomes following different anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatments in subretinal neovascular membrane secondary to type 2 proliferative macular telangiectasia.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020 Jan;258(1):99-106. doi: 10.1007/s00417-019-04520-x. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 31768680
-
Pars plana vitrectomy combined with focal endolaser photocoagulation for idiopathic macular telangiectasia.Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:786578. doi: 10.1155/2014/786578. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Case Rep Med. 2014. PMID: 24876845 Free PMC article.
-
Ganglion Cell Complex Evaluation in Exudative Age-Related Macular Degeneration after Repeated Intravitreal Injections of Ranibizumab.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:268796. doi: 10.1155/2015/268796. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26167478 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Imaging Findings and Treatment with Dexamethasone Implant in Three Cases of Idiopathic Macular Telangiectasia Type 1.Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr 6;12(1):92-97. doi: 10.1159/000509850. eCollection 2021 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33976663 Free PMC article.
-
EFFICACY OF INTRAVITREAL AFLIBERCEPT IN MACULAR TELANGIECTASIA TYPE 1 IS LINKED TO THE OCULAR ANGIOGENIC PROFILE.Retina. 2017 Dec;37(12):2226-2237. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001424. Retina. 2017. PMID: 28002269 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tasca J, Grogg JA. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasia: a review and case report. Clin Eye Vis Care. 2000;12:79–87. - PubMed
-
- Gass JD, Blodi BA. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Update of classification and follow-up study. Ophthalomology. 1993;100:1536–1546. - PubMed
-
- Gass JD, Oyakawa RT. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1982;10:769–780. - PubMed
-
- Abujarra S, Bonanomi MT, Cresta FB, Machado CG, Pimentel SL, Caramelli CB. Idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis: Clinical pattern in 19 cases. Ophthalmologica. 2000;214:406–411. - PubMed
-
- Issacs TW, McAllister IL. Familial idiopathic juxtafoveolar retinal telangiectasis. Eye. 1996;10:639–642. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

