In vivo regulation of E2F1 by Polycomb group genes in Drosophila
- PMID: 23275887
- PMCID: PMC3516486
- DOI: 10.1534/g3.112.004333
In vivo regulation of E2F1 by Polycomb group genes in Drosophila
Abstract
The E2F transcription factors are important regulators of the cell cycle whose function is commonly misregulated in cancer. To identify novel regulators of E2F1 activity in vivo, we used Drosophila to conduct genetic screens. For this, we generated transgenic lines that allow the tissue-specific depletion of dE2F1 by RNAi. Expression of these transgenes using Gal4 drivers in the eyes and wings generated reliable and modifiable phenotypes. We then conducted genetic screens testing the capacity of Exelixis deficiencies to modify these E2F1-RNAi phenotypes. From these screens, we identified mutant alleles of Suppressor of zeste 2 [Su(z)2] and multiple Polycomb group genes as strong suppressors of the E2F1-RNA interference phenotypes. In validation of our genetic data, we find that depleting Su(z)2 in cultured Drosophila cells restores the cell-proliferation defects caused by reduction of dE2F1 by elevating the level of dE2f1. Furthermore, analyses of methylation status of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me) from the published modENCODE data sets suggest that the genomic regions harboring dE2f1 gene and certain dE2f1 target genes display H3K27me during development and in several Drosophila cell lines. These in vivo observations suggest that the Polycomb group may regulate cell proliferation by repressing the transcription of dE2f1 and certain dE2F1 target genes. This mechanism may play an important role in coordinating cellular differentiation and proliferation during Drosophila development.
Keywords: Drosophila; E2F1; PcG; Su(z)2; cell proliferation.
Figures
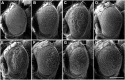
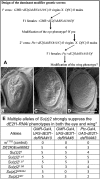
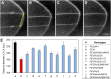
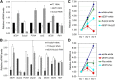
Similar articles
-
Drosophila GAGA factor is required for full activation of the dE2f1-Yki/Sd transcriptional program.Cell Cycle. 2012 Nov 15;11(22):4191-202. doi: 10.4161/cc.22486. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 23070566 Free PMC article.
-
Ash1 counteracts Polycomb repression independent of histone H3 lysine 36 methylation.EMBO Rep. 2019 Apr;20(4):e46762. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846762. Epub 2019 Mar 4. EMBO Rep. 2019. PMID: 30833342 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo analysis of Drosophila SU(Z)12 function.Mol Genet Genomics. 2008 Feb;279(2):159-70. doi: 10.1007/s00438-007-0304-3. Epub 2007 Nov 22. Mol Genet Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18034266
-
Epigenetic Regulation by Polycomb Complexes from Drosophila to Human and Its Relation to Communicable Disease Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 14;23(20):12285. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012285. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polycomb and Trithorax Group Genes in Drosophila.Genetics. 2017 Aug;206(4):1699-1725. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.185116. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28778878 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis of RB-loss identifies widespread cellular programming and synthetic weaknesses.Commun Biol. 2021 Aug 17;4(1):977. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02495-2. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34404904 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic factor EPC1 is a master regulator of DNA damage response by interacting with E2F1 to silence death and activate metastasis-related gene signatures.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 8;44(1):117-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv885. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26350215 Free PMC article.
-
Effete, an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme with multiple roles in Drosophila development and chromatin organization.Fly (Austin). 2013 Oct-Dec;7(4):256-62. doi: 10.4161/fly.26567. Epub 2013 Oct 2. Fly (Austin). 2013. PMID: 24088712 Free PMC article.
-
A developmental genetic analysis of the lysine demethylase KDM2 mutations in Drosophila melanogaster.Mech Dev. 2014 Aug;133:36-53. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2014.06.003. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Mech Dev. 2014. PMID: 25016215 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of Abd-B by Polycomb is critical for cell identity maintenance in adult Drosophila testis.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 11;7(1):5101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05359-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28698559 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attwooll C., Oddi S., Cartwright P., Prosperini E., Agger K., et al. , 2005. A novel repressive E2F6 complex containing the polycomb group protein, EPC1, that interacts with EZH2 in a proliferation-specific manner. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 1199–1208 - PubMed
-
- Ballestar E., Esteller M., 2008. Epigenetic gene regulation in cancer. Adv. Genet. 61: 247–267 - PubMed
-
- Bracken A. P., Helin K., 2009. Polycomb group proteins: navigators of lineage pathways led astray in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9: 773–784 - PubMed
-
- Brand A. H., Manoukian A. S., Perrimon N., 1994. Ectopic expression in Drosophila. Methods Cell Biol. 44: 635–654 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
