Molecular mechanisms of appetite regulation
- PMID: 23275931
- PMCID: PMC3530708
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.391
Molecular mechanisms of appetite regulation
Abstract
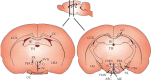
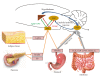
The prevalence of obesity has been rapidly increasing worldwide over the last several decades and has become a major health problem in developed countries. The brain, especially the hypothalamus, plays a key role in the control of food intake by sensing metabolic signals from peripheral organs and modulating feeding behaviors. To accomplish these important roles, the hypothalamus communicates with other brain areas such as the brainstem and reward-related limbic pathways. The adipocyte-derived hormone leptin and pancreatic β-cell-derived insulin inform adiposity to the hypothalamus. Gut hormones such as cholecystokinin, peptide YY, pancreatic polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide 1, and oxyntomodulin transfer satiety signals to the brain and ghrelin relays hunger signals. The endocannabinoid system and nutrients are also involved in the physiological regulation of food intake. In this article, we briefly review physiological mechanisms of appetite regulation.
Keywords: Adiposity; Appetite; Hypothalamus; Leptin; Satiety.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Obesity and appetite control.Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012:824305. doi: 10.1155/2012/824305. Epub 2012 Aug 1. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012. PMID: 22899902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroendocrine control of food intake.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008 Feb;18(2):158-68. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2007.06.004. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2008. PMID: 18061414 Review.
-
How palatable food disrupts appetite regulation.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005 Aug;97(2):61-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7843.2005.pto_179.x. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2005. PMID: 15998351 Review.
-
Appetite regulation: an overview.Thyroid. 2007 May;17(5):433-45. doi: 10.1089/thy.2007.0018. Thyroid. 2007. PMID: 17542673 Review.
-
Gut hormones and the control of appetite.Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Aug;15(6):259-63. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2004.06.002. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15358278 Review.
Cited by
-
Weight Regain after Metabolic Surgery: Beyond the Surgical Failure.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 18;13(4):1143. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041143. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormalities in Glucose Metabolism, Appetite-Related Peptide Release, and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Play a Central Role in Appetite Disorders in Peritoneal Dialysis.Front Physiol. 2019 May 28;10:630. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.00630. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31191339 Free PMC article.
-
The association between dietary habits and self-care behavior of pregnant women with pregnancy complications.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 24;14(1):19681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70162-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39181929 Free PMC article.
-
Self-Reported Eating Speed and Incidence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: the Japan Environment and Children's Study.Nutrients. 2020 May 2;12(5):1296. doi: 10.3390/nu12051296. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32370156 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Capsaicin Protects Cardiometabolic Organs from Dysfunction.Nutrients. 2016 Apr 25;8(5):174. doi: 10.3390/nu8050174. Nutrients. 2016. PMID: 27120617 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Obesity. Geneva: WHO; 2008.
-
- Must A, Spadano J, Coakley EH, Field AE, Colditz G, Dietz WH. The disease burden associated with overweight and obesity. JAMA. 1999;282:1523–1529. - PubMed
-
- Heisler LK, Cowley MA, Tecott LH, Fan W, Low MJ, Smart JL, Rubinstein M, Tatro JB, Marcus JN, Holstege H, Lee CE, Cone RD, Elmquist JK. Activation of central melanocortin pathways by fenfluramine. Science. 2002;297:609–611. - PubMed
-
- Huszar D, Lynch CA, Fairchild-Huntress V, Dunmore JH, Fang Q, Berkemeier LR, Gu W, Kesterson RA, Boston BA, Cone RD, Smith FJ, Campfield LA, Burn P, Lee F. Targeted disruption of the melanocortin-4 receptor results in obesity in mice. Cell. 1997;88:131–141. - PubMed
-
- Tao YX. Molecular mechanisms of the neural melanocortin receptor dysfunction in severe early onset obesity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2005;239:1–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

