Discovery of STL polyomavirus, a polyomavirus of ancestral recombinant origin that encodes a unique T antigen by alternative splicing
- PMID: 23276405
- PMCID: PMC3693558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.12.005
Discovery of STL polyomavirus, a polyomavirus of ancestral recombinant origin that encodes a unique T antigen by alternative splicing
Erratum in
- Virology. 2013 May 10;439(2):163-4
Abstract
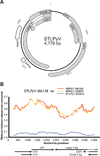
The family Polyomaviridae is comprised of circular double-stranded DNA viruses, several of which are associated with diseases, including cancer, in immunocompromised patients. Here we describe a novel polyomavirus recovered from the fecal microbiota of a child in Malawi, provisionally named STL polyomavirus (STLPyV). We detected STLPyV in clinical stool specimens from USA and The Gambia at up to 1% frequency. Complete genome comparisons of two STLPyV strains demonstrated 5.2% nucleotide divergence. Alternative splicing of the STLPyV early region yielded a unique form of T antigen, which we named 229T, in addition to the expected large and small T antigens. STLPyV has a mosaic genome and shares an ancestral recombinant origin with MWPyV. The discovery of STLPyV highlights a novel alternative splicing strategy and advances our understanding of the complex evolutionary history of polyomaviruses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Babakir-Mina M, Ciccozzi M, Perno CF, Ciotti M. The novel KI, WU, MC polyomaviruses: possible human pathogens? New Microbiol. 2011;34:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee S. Evolutionary interrelationships among polyomaviruses based on nucleotide and amino acid variations. Indian Journal of Biotechnology. 2010;9:252–264.
-
- Bialasiewicz S, Rockett R, Whiley DW, Abed Y, Allander T, Binks M, Boivin G, Cheng AC, Chung JY, Ferguson PE, Gilroy NM, Leach AJ, Lindau C, Rossen JW, Sorrell TC, Nissen MD, Sloots TP. Whole-genome characterization and genotyping of global WU polyomavirus strains. J Virol. 2010;84:6229–6234. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

