Cloning and characterization of a microsomal epoxide hydrolase from Heliothis virescens
- PMID: 23276675
- PMCID: PMC3577957
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2012.12.002
Cloning and characterization of a microsomal epoxide hydrolase from Heliothis virescens
Abstract
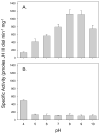
Epoxide hydrolases (EHs) are α/β-hydrolase fold superfamily enzymes that convert epoxides to 1,2-trans diols. In insects EHs play critical roles in the metabolism of toxic compounds and allelochemicals found in the diet and for the regulation of endogenous juvenile hormones (JHs). In this study we obtained a full-length cDNA, hvmeh1, from the generalist feeder Heliothis virescens that encoded a highly active EH, Hv-mEH1. Of the 10 different EH substrates that were tested, Hv-mEH1 showed the highest specific activity (1180 nmol min(-1) mg(-1)) for a 1,2-disubstituted epoxide-containing fluorescent substrate. This specific activity was more than 25- and 3900-fold higher than that for the general EH substrates cis-stilbene oxide and trans-stilbene oxide, respectively. Although phylogenetic analysis placed Hv-mEH1 in a clade with some lepidopteran JH metabolizing EHs (JHEHs), JH III was a relatively poor substrate for Hv-mEH1. Hv-mEH1 showed a unique substrate selectivity profile for the substrates tested in comparison to those of MsJHEH, a well-characterized JHEH from Manduca sexta, and hmEH, a human microsomal EH. Hv-mEH1 also showed unique enzyme inhibition profiles to JH-like urea, JH-like secondary amide, JH-like primary amide, and non-JH-like primary amide compounds in comparison to MsJHEH and hmEH. Although Hv-mEH1 is capable of metabolizing JH III, our findings suggest that this enzymatic activity does not play a significant role in the metabolism of JH in the caterpillar. The ability of Hv-mEH1 to rapidly hydrolyze 1,2-disubstituted epoxides suggests that it may play roles in the metabolism of fatty acid epoxides such as those that are commonly found in the diet of Heliothis.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of Hovi-mEH1, a microsomal epoxide hydrolase from the glassy-winged sharpshooter Homalodisca vitripennis.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013 Aug;83(4):171-9. doi: 10.1002/arch.21100. Epub 2013 May 23. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23704009 Free PMC article.
-
Juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase. Photoaffinity labeling, purification, and characterization from tobacco hornworm eggs.J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19604-9. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 8396141
-
Expression and characterization of the recombinant juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) from Manduca sexta.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1998 May-Jun;28(5-6):409-19. doi: 10.1016/s0965-1748(98)00014-9. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9692241
-
Biochemistry of proteins that bind and metabolize juvenile hormones.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996;32(3-4):407-19. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6327(1996)32:3/4<407::AID-ARCH13>3.0.CO;2-G. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8756303 Review.
-
Gerry Brooks and epoxide hydrolases: four decades to a pharmaceutical.Pest Manag Sci. 2008 Jun;64(6):594-609. doi: 10.1002/ps.1583. Pest Manag Sci. 2008. PMID: 18383502 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation Roles of Juvenile Hormone Epoxide Hydrolase Gene 2 in the Female River Prawn Macrobrachium nipponense Reproductive Process.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Nov 25;46(12):13456-13470. doi: 10.3390/cimb46120803. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39727931 Free PMC article.
-
Development of potent inhibitors of the human microsomal epoxide hydrolase.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 May 1;193:112206. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112206. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32203787 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and characterization of an epoxide hydrolase from Anopheles gambiae with high activity on epoxy fatty acids.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014 Nov;54:42-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2014.08.004. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25173592 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Hovi-mEH1, a microsomal epoxide hydrolase from the glassy-winged sharpshooter Homalodisca vitripennis.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013 Aug;83(4):171-9. doi: 10.1002/arch.21100. Epub 2013 May 23. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23704009 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Degradation of Juvenile Hormone Promotes Reproductive Diapause in the Predatory Ladybeetle Coccinella Septempunctata.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 29;13:877153. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.877153. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35574499 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdel-Aal YAI, Hammock BD. 3-Octylthio-1,1,1-trifluoro-2-propanone, a high affinity and slow binding inhibitor of juvenile hormone esterase from Trichoplusia ni (Hubner) Insect Biochem. 1985;15:111–122.
-
- Borhan B, Mebrahtu T, Nazarian S, Kurth MJ, Hammock BD. Improved radiolabeled substrates for soluble epoxide hydrolase. Anal Biochem. 1995;231:188–200. - PubMed
-
- Casas J, Harshman LG, Hammock BD. Epoxide hydrolase activity on juvenile hormone in Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. 1991;21:17–26.
-
- Debernard S, Morisseau C, Severson TF, Feng L, Wojtasek H, Prestwich GD, Hammock BD. Expression and characterization of the recombinant juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase (JHEH) from Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1998;28:409–419. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

