Solubility-based genetic screen identifies RING finger protein 126 as an E3 ligase for activation-induced cytidine deaminase
- PMID: 23277564
- PMCID: PMC3549133
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1214538110
Solubility-based genetic screen identifies RING finger protein 126 as an E3 ligase for activation-induced cytidine deaminase
Abstract
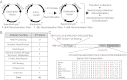
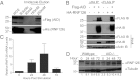
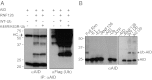
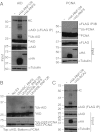
Protein-protein interactions are typically identified by either biochemical purification coupled to mass spectrometry or genetic approaches exemplified by the yeast two-hybrid assay; however, neither assay works well for the identification of cofactors for poorly soluble proteins. Solubility of a poorly soluble protein is thought to increase upon cofactor binding, possibly by masking otherwise exposed hydrophobic domains. We have exploited this notion to develop a high-throughput genetic screen to identify interacting partners of an insoluble protein fused to chloramphenicol acetyltransferase by monitoring the survival of bacteria in the presence of a drug. In addition to presenting proof-of-principle experiments, we apply this screen to activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), a poorly soluble protein that is essential for antibody diversification. We identify a unique cofactor, RING finger protein 126 (RNF126), verify its interaction by traditional techniques, and show that it has functional consequences as RNF126 is able to ubiquitylate AID. Our results underpin the value of this screening technique and suggest a unique form of AID regulation involving RNF126 and ubiquitylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CUL7 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Mediates the Degradation of Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase and Regulates the Ig Class Switch Recombination in B Lymphocytes.J Immunol. 2019 Jul 1;203(1):269-281. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900125. Epub 2019 May 15. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31092637
-
Mulan E3 ubiquitin ligase interacts with multiple E2 conjugating enzymes and participates in mitophagy by recruiting GABARAP.Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2921-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.004. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25224329
-
Molecular dissection of a rice microtubule-associated RING finger protein and its potential role in salt tolerance in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Nov;89(4-5):365-84. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0375-1. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26358044
-
TRIM proteins as RING finger E3 ubiquitin ligases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;770:27-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5398-7_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23630998 Review.
-
The prolific ATL family of RING-H2 ubiquitin ligases.Plant Signal Behav. 2012 Aug;7(8):1014-21. doi: 10.4161/psb.20851. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Plant Signal Behav. 2012. PMID: 22827943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
E3 Ubiquitin ligase RNF126 regulates the progression of tongue cancer.Cancer Med. 2016 Aug;5(8):2043-7. doi: 10.1002/cam4.771. Epub 2016 May 26. Cancer Med. 2016. PMID: 27227488 Free PMC article.
-
Ring finger protein 126: a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2021 May;36(5):559-566. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-328. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Histol Histopathol. 2021. PMID: 33724438
-
Transcriptional stalling in B-lymphocytes: a mechanism for antibody diversification and maintenance of genomic integrity.Transcription. 2013 May-Jun;4(3):127-35. doi: 10.4161/trns.24556. Epub 2013 Apr 12. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23584095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNF126 as a Biomarker of a Poor Prognosis in Invasive Breast Cancer and CHEK1 Inhibitor Efficacy in Breast Cancer Cells.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 1;24(7):1629-1643. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2242. Epub 2018 Jan 11. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29326282 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on SNPs of Human Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase AID.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 25;26(13):6107. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136107. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649888 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fields S, Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989;340(6230):245–246. - PubMed
-
- Ghavidel A, Cagney G, Emili A. A skeleton of the human protein interactome. Cell. 2005;122(6):830–832. - PubMed
-
- Rual J-F, et al. Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature. 2005;437(7062):1173–1178. - PubMed
-
- Alber F, et al. Determining the architectures of macromolecular assemblies. Nature. 2007;450(7170):683–694. - PubMed
-
- Gavin A-C, et al. Proteome survey reveals modularity of the yeast cell machinery. Nature. 2006;440(7084):631–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

