Energetic cost of protein import across the envelope membranes of chloroplasts
- PMID: 23277572
- PMCID: PMC3549074
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1115886110
Energetic cost of protein import across the envelope membranes of chloroplasts
Abstract
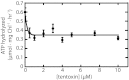
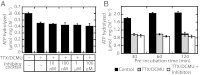
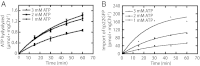
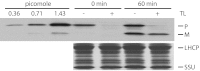
Chloroplasts are the organelles of green plants in which light energy is transduced into chemical energy, forming ATP and reduced carbon compounds upon which all life depends. The expenditure of this energy is one of the central issues of cellular metabolism. Chloroplasts contain ~3,000 proteins, among which less than 100 are typically encoded in the plastid genome. The rest are encoded in the nuclear genome, synthesized in the cytosol, and posttranslationally imported into the organelle in an energy-dependent process. We report here a measurement of the amount of ATP hydrolyzed to import a protein across the chloroplast envelope membranes--only the second complete accounting of the cost in Gibbs free energy of protein transport to be undertaken. Using two different precursors prepared by three distinct techniques, we show that the import of a precursor protein into chloroplasts is accompanied by the hydrolysis of ~650 ATP molecules. This translates to a ΔG(protein) (transport) of some 27,300 kJ/mol protein imported. We estimate that protein import across the plastid envelope membranes consumes ~0.6% of the total light-saturated energy output of the organelle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization and isolation of the chloroplast protein import machinery.Methods Cell Biol. 1995;50:255-67. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61035-3. Methods Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 8531798 No abstract available.
-
Homologous and heterologous reconstitution of Golgi to chloroplast transport and protein import into the complex chloroplasts of Euglena.J Cell Sci. 2005 Apr 15;118(Pt 8):1651-61. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02277. Epub 2005 Mar 29. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15797929
-
Protein targeting across and into chloroplast membranes.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;684:139-57. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-925-3_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20960128
-
Toc, tic, and chloroplast protein import.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jun 12;1590(1-3):177-89. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00176-3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12180471 Review.
-
Toc, Tic, and chloroplast protein import.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Dec 12;1541(1-2):64-79. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(01)00147-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001. Corrected and republished in: Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jun 12;1590(1-3):177-89. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(02)00176-3. PMID: 11750663 Corrected and republished. Review.
Cited by
-
Charge-dependent secretion of an intrinsically disordered protein via the autotransporter pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Nov 5;110(45):E4246-55. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310345110. Epub 2013 Oct 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24145447 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of bacterial autotransporter assembly using purified components.Elife. 2014 Sep 2;3:e04234. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04234. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25182416 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma biomarkers in patients with age-related sarcopenia: a proteomic exploration and experimental validation.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Dec 27;37(1):13. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02903-7. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 39725826 Free PMC article.
-
The Principles of Protein Targeting and Transport Across Cell Membranes.Protein J. 2019 Jun;38(3):236-248. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09847-2. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 31187382 Review.
-
Protein import into chloroplasts and its regulation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Feb 28;48(1):71-82. doi: 10.1042/BST20190274. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 31922184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schatz G, Dobberstein B. Common principles of protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1996;271(5255):1519–1526. - PubMed
-
- Mori T, Ishitani R, Tsukazaki T, Nureki O, Sugita Y. Molecular mechanisms underlying the early stage of protein translocation through the Sec translocon. Biochemistry. 2010;49(5):945–950. - PubMed
-
- Driessen AJ, Nouwen N. Protein translocation across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 2008;77:643–667. - PubMed
-
- Alder NN, Theg SM. Energy use by biological protein transport pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28(8):442–451. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AE, Haigh NG. The ER translocon and retrotranslocation: Is the shift into reverse manual or automatic? Cell. 2000;102(6):709–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

