Environmental perturbations lift the degeneracy of the genetic code to regulate protein levels in bacteria
- PMID: 23277573
- PMCID: PMC3568297
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1211077110
Environmental perturbations lift the degeneracy of the genetic code to regulate protein levels in bacteria
Abstract
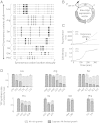
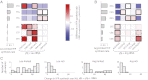
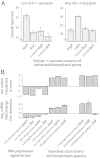
The genetic code underlying protein synthesis is a canonical example of a degenerate biological system. Degeneracies in physical and biological systems can be lifted by external perturbations, thus allowing degenerate systems to exhibit a wide range of behaviors. Here we show that the degeneracy of the genetic code is lifted by environmental perturbations to regulate protein levels in living cells. By measuring protein synthesis rates from a synthetic reporter library in Escherichia coli, we find that environmental perturbations, such as reduction of cognate amino acid supply, lift the degeneracy of the genetic code by splitting codon families into a hierarchy of robust and sensitive synonymous codons. Rates of protein synthesis associated with robust codons are up to 100-fold higher than those associated with sensitive codons under these conditions. We find that the observed hierarchy between synonymous codons is not determined by usual rules associated with tRNA abundance and codon usage. Rather, competition among tRNA isoacceptors for aminoacylation underlies the robustness of protein synthesis. Remarkably, the hierarchy established using the synthetic library also explains the measured robustness of synthesis for endogenous proteins in E. coli. We further found that the same hierarchy is reflected in the fitness cost of synonymous mutations in amino acid biosynthesis genes and in the transcriptional control of σ-factor genes. Our study suggests that organisms can exploit degeneracy lifting as a general strategy to adapt protein synthesis to their environment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shankar R. Principles of Quantum Mechanics. 2nd Ed. New York: Plenum; 1994.
-
- Baer M, Billing GD. The Role of Degenerate States in Chemistry. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley; 2002.
-
- Cowan RD. The Theory of Atomic Structure and Spectra. Berkeley: Univ of California Press; 1981.
-
- Affleck I, Ludwig AWW. Universal noninteger “ground-state degeneracy” in critical quantum systems. Phys Rev Lett. 1991;67(2):161–164. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

