Epidural anesthesia and postoperatory analgesia with alpha-2 adrenergic agonists and lidocaine for ovariohysterectomy in bitches
- PMID: 23277701
- PMCID: PMC3384285
Epidural anesthesia and postoperatory analgesia with alpha-2 adrenergic agonists and lidocaine for ovariohysterectomy in bitches
Abstract
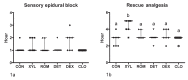
The aim of this study was to determine the viability and cardiorespiratory effects of the association of epidural alpha-2 adrenergic agonists and lidocaine for ovariohysterectomy (OH) in bitches. Forty-two bitches were spayed under epidural anesthesia with 2.5 mg/kg body weight (BW) of 1% lidocaine with adrenaline (CON) or in association with 0.25 mg/kg BW of xylazine (XYL), 10 μg/kg BW of romifidine (ROM), 30 μg/kg BW of detomidine (DET), 2 μg/kg BW of dexmedetomidine (DEX), or 5 μg/kg BW of clonidine (CLO). Heart rate (HR), respiratory rate (fR) and arterial pressures were monitored immediately before and every 10 min after the epidural procedure. Blood gas and pH analysis were done before, and at 30 and 60 min after the epidural procedure. Animals were submitted to isoflurane anesthesia if they presented a slightest sign of discomfort during the procedure. Time of sensory epidural block and postoperative analgesia were evaluated. All animals in CON and DEX, 5 animals in ROM and CLO, 4 animals in XYL, and 3 in DET required supplementary isoflurane. All groups, except CLO, showed a decrease in HR. There was an increase in arterial pressures in all groups. Postoperative analgesia lasted the longest in XYL. None of the protocols were totally efficient to perform the complete procedure of OH; however, xylazine provided longer postoperative analgesia than the others.
L’objectif de la présente étude était de déterminer l’efficacité et les effets cardio-respiratoires d’une anesthésie épidurale par combinaison d’agonistes adrénergiques alpha-2 et de lidocaïne pour effectuer une hystéro-ovariectomie (OH) chez des chiennes. Quarante-deux chiennes ont été châtrées sous anesthésie épidurale réalisée avec de la lidocaïne 1 % à un dosage de 2,5 mg/kg de poids vif (BW) avec de l’adrénaline (CON) ou en association avec 0,25 mg/kg BW de xylazine (XYL), 10 μg/kg BW de romifidine (ROM), 30 μg/kg BW de detomidine (DET), 2 μg/kg de dexmedetomidine (DEX), ou 5 μg/kg BW de clonidine (CLO). La fréquence cardiaque (HR), le rythme respiratoire (fR) et la pression artérielle ont été mesurés immédiatement avant et à des intervalles de 10 minutes après la procédure épidurale. Des analyses des gaz sanguins et du pH ont été effectuées avant et 30 et 60 minutes après la procédure épidurale. Les animaux ont été mis sous anesthésie à l’isoflurane s’ils présentaient le moindre signe d’inconfort durant la procédure. La durée du temps de blocage sensitif et d’analgésie postopératoire a été évaluée. Tous les animaux CON et DEX, 5 animaux ROM et CLO, 4 animaux XYL et 3 animaux DET ont nécessité de l’isoflurane. Tous les groupes, sauf le groupe CLO, ont présenté une réduction de HR. Il y a eu une augmentation de la pression artérielle dans tous les groupes. L’analgésie post-opératoire a été la plus longue dans le groupe XYL. Aucun des protocoles n’était complètement efficace pour permettre la procédure complète d’OH; toutefois, la xylazine a fourni une analgésie post-opératoire plus longue que les autres médicaments.
Traduit par Docteur Serge Messier
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of analgesic, sympathetic and motor effects of 1% and 2% lidocaine administered epidurally in dogs undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2020 Nov;47(6):797-802. doi: 10.1016/j.vaa.2020.07.034. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2020. PMID: 32900618
-
Effects of tramadol alone, in combination with meloxicam or dipyrone, on postoperative pain and the analgesic requirement in dogs undergoing unilateral mastectomy with or without ovariohysterectomy.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013 Nov;40(6):641-9. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12080. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23910901 Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative analgesic effects of either a constant rate infusion of fentanyl, lidocaine, ketamine, dexmedetomidine, or the combination lidocaine-ketamine-dexmedetomidine after ovariohysterectomy in dogs.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2015 May;42(3):309-18. doi: 10.1111/vaa.12215. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2015. PMID: 25039918 Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiopulmonary and isoflurane-sparing effects of epidural or intravenous infusion of dexmedetomidine in cats undergoing surgery with epidural lidocaine.Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010 Mar;37(2):106-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-2995.2009.00512.x. Vet Anaesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 20230560 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of intrarectal ozone, ozone administered in acupoints and meloxicam for postoperative analgesia in bitches undergoing ovariohysterectomy.Vet J. 2013 Sep;197(3):794-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2013.05.015. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Vet J. 2013. PMID: 23810742 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
An Update on Drugs Used for Lumbosacral Epidural Anesthesia and Analgesia in Dogs.Front Vet Sci. 2017 May 12;4:68. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2017.00068. eCollection 2017. Front Vet Sci. 2017. PMID: 28553642 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine Premedication in Balanced Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 14;11(11):3254. doi: 10.3390/ani11113254. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of different analgesic techniques on hemodynamic variables recorded with an esophageal Doppler monitor during ovariohysterectomy in dogs.Can Vet J. 2018 Apr;59(4):419-424. Can Vet J. 2018. PMID: 29606730 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valverde A. Epidural analgesia and anesthesia in dogs and cats. Vet Clin N Am Small. 2008;38:1205–1230. - PubMed
-
- Ellenport CR. Aparelho urogenital do carnívoro. In: Sisson S, Grossman JD, editors. Anatomia dos animais domésticos. 5th ed. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Guanabara Koogan; 1986. pp. 1481–1493.
-
- Gasparini SS, Luna SPL, Cassu RN, Uiechi E, Crocci AJ. Epidural anaesthesia using ropivacaine, lidocaine or the combination of lidocaine and xylazine in dogs. Cardiorespiratory and analgesic effects. Cienc Rural. 2007;37:418–424.
-
- Aminkov B, Zlateva N. Epidural anesthesia for castration of the bitch. Bulg J Vet Med. 2004;7:113–119.
-
- Brondani JT, Natalini CC, Raiser AG, Mazzanti A, Prati L. Epidural analgesia with clonidine or romifidine in dogs submitted to coxofemoral surgery. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec. 2004;56:175–182.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
