Study of C-reactive protein and myocardial infarction in the Indian population
- PMID: 23277716
- PMCID: PMC3286588
- DOI: 10.1007/s12291-011-0164-9
Study of C-reactive protein and myocardial infarction in the Indian population
Abstract
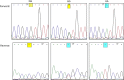
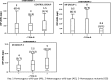
To analyse the association of high sensitivity C-reactive (hsCRP) protein levels and -717A/G single nucleotide polymorphism of CRP with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in the Indian population. Study population included 100 MI cases wherein 32 patients had experienced previous MI (MI-Group-1), 68 MI cases were recruited at presentation (MI-Group-2) and equal number of age and gender matched healthy individuals. hsCRP levels were determined by ELISA and genotyping of -717A/G was carried out by polymerase chain reaction-based restriction digestion method. The -717A/G genotypes did not influence hsCRP level and their distribution did not differ between groups. However, in the present study hsCRP demonstrated significant correlation with BMI in controls of both the genders and with triglycerides in females of AMI at presentation who otherwise are with low risk profile. Identifying traditional risk factors associated with inflammation may help in controlling the acute event.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Indian population; Myocardial infarction; Single nucleotide polymorphism.
Figures




References
-
- Enas A Enas, Senthilkumar A. Coronary artery disease in Asian Indians: an update and review. Internet J Cardiol. 2001;1(2): [about 71 p]. www.ispub.com/journal/the_internet_journal_of_cardiology/archive/volume.
-
- Pearson TA, Mensah GA et al. AHA/CDC scientific statement on markers of inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2003; 107:499–511. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
