Pharmacokinetic analysis of oral doxycycline in rhesus macaques
- PMID: 23278524
- PMCID: PMC3593953
- DOI: 10.1111/jmp.12031
Pharmacokinetic analysis of oral doxycycline in rhesus macaques
Abstract
Background: Following administration of an antibiotic, the concentration in blood changes over time and is dependent on the type of antibiotic, the route and species of the individual. The most relevant pharmacodynamic property of a bacteriostatic antibiotic such as doxycycline is the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), whereas pharmacokinetics may include rates of absorption and elimination from blood.
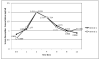
Methods: We determined serum concentrations of doxycycline following administration of 5 mg/kg in two macaques.
Results: The area under the concentration-time curve over 24 hours (AUC0-24 ) following two doses was extrapolated from the curve over 12 hours following a single dose, with the purpose of calculating the AUC0-24 :MIC.
Conclusions: Other than a somewhat faster rate of elimination, the PK-PD values for doxycycline in macaques appears similar to those determined for humans. This information will be valuable for treating disease in macaques and for research in bacterial infection models that use macaques.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Similar articles
-
PK and PK/PD of doxycycline in drinking water after therapeutic use in pigs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Dec;28(6):525-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2885.2005.00700.x. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 16343284
-
Integration of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic for dose optimization of doxycycline against Haemophilus parasuis in pigs.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Oct;41(5):706-718. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12512. Epub 2018 Apr 25. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29696661
-
Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of doxycycline in ostriches (Struthio camelus) at two different dose rates.J Vet Sci. 2006 Dec;7(4):327-32. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.4.327. J Vet Sci. 2006. PMID: 17106222 Free PMC article.
-
Reappraisal of Contemporary Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Principles for Informing Aminoglycoside Dosing.Pharmacotherapy. 2018 Dec;38(12):1229-1238. doi: 10.1002/phar.2193. Pharmacotherapy. 2018. PMID: 30403305 Review.
-
How predictive is PK/PD for antibacterial agents?Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002 Apr;19(4):333-9. doi: 10.1016/s0924-8579(02)00029-8. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002. PMID: 11978504 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of Organoids to Study Infectious Host Interactions.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2742:151-164. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3561-2_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38165622
-
Critical analysis of a doxycycline treatment trial of rhesus macaques infected with Borrelia burgdorferi.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;92(3):183-188. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2018.06.007. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30017315 Free PMC article.
-
Late Disseminated Lyme Disease: Associated Pathology and Spirochete Persistence Posttreatment in Rhesus Macaques.Am J Pathol. 2018 Mar;188(3):672-682. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Am J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29242055 Free PMC article.
-
Superior efficacy of combination antibiotic therapy versus monotherapy in a mouse model of Lyme disease.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 21;14:1293300. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1293300. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38075920 Free PMC article.
-
Borreliella burgdorferi Antimicrobial-Tolerant Persistence in Lyme Disease and Posttreatment Lyme Disease Syndromes.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0344021. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03440-21. Epub 2022 Apr 25. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35467428 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agwuh KN, MacGowan A. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the tetracyclines including glycylcyclines. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2006;58:256–265. - PubMed
-
- Ambrose PG, Bhavnani SB, Rubino CM, Louie A, Gumbo T, Forrest A. Pharmacokinetics-pharmacodynamics of antimicrobial therapy: it’s not just for mice anymore. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2007:79–86. - PubMed
-
- Andes D, Anon J, Jacobs MR, Craig WA. Application of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics to antimicrobial therapy of respiratory tract infections. Clin Lab Med. 2004;24:477–502. - PubMed
-
- Andes D, Craig WA. Animal model pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics: a critical review. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2002;19:261–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical