Identification of DPAGT1 as a new gene in which mutations cause a congenital myasthenic syndrome
- PMID: 23278575
- PMCID: PMC6044425
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2012.06790.x
Identification of DPAGT1 as a new gene in which mutations cause a congenital myasthenic syndrome
Abstract
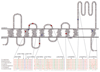
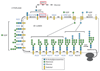
Congenital myasthenic syndromes (CMS) are a group of inherited disorders that arise from impaired signal transmission at the neuromuscular synapse. They are characterized by fatigable muscle weakness. This is a heterogenous group of disorders with 15 different genes implicated in the development of the disease. Using whole-exome sequencing we identified DPAGT1 as a new gene associated with CMS. DPAGT1 catalyses the first step of N-linked protein glycosylation. DPAGT1 patients are characterized by weakness of limb muscles, response to treatment with cholinesterase inhibitors, and the presence of tubular aggregates on muscle biopsy. We showed that DPAGT1 is required for glycosylation of acetylcholine receptor (AChR) subunits and efficient export of AChR to the cell surface. We suggest that the primary pathogenic mechanism of DPAGT1-associated CMS is reduced levels of AChRs at the endplate region. This finding demonstrates that impairment of the N-linked glycosylation pathway can lead to the development of CMS.
© 2012 New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chaouch A, Beeson D, Hantai D, Lochmuller H. 186th ENMC international workshop: congenital myasthenic syndromes 24–26 June 2011, Naarden, The Netherlands. Neuromuscul Disord. 2012;22:566–576. - PubMed
-
- Guergueltcheva V, et al. Congenital myasthenic syndrome with tubular aggregates caused by GFPT1 mutations. J Neurol. 2012;259:838–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

