Differential role of lipocalin 2 during immune complex-mediated acute and chronic inflammation in mice
- PMID: 23280250
- PMCID: PMC3618508
- DOI: 10.1002/art.37840
Differential role of lipocalin 2 during immune complex-mediated acute and chronic inflammation in mice
Abstract
Objective: Lipocalin 2 (LCN-2) is an innate immune protein that is expressed by a variety of cells and is highly up-regulated during several pathologic conditions, including immune complex (IC)-mediated inflammatory/autoimmune disorders. However, the function of LCN-2 during IC-mediated inflammation is largely unknown. Therefore, this study was undertaken to investigate the role of LCN-2 in IC-mediated diseases.
Methods: The up-regulation of LCN-2 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 3 different mouse models of IC-mediated autoimmune disease: systemic lupus erythematosus, collagen-induced arthritis, and serum-transfer arthritis. The in vivo role of LCN-2 during IC-mediated inflammation was investigated using LCN-2-knockout mice and their wild-type littermates.
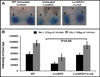
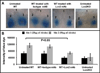
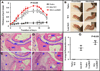
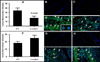
Results: LCN-2 levels were significantly elevated in all 3 of the autoimmune disease models. Further, in an acute skin inflammation model, LCN-2-knockout mice exhibited a 50% reduction in inflammation, with histopathologic analysis revealing notably reduced immune cell infiltration as compared to wild-type mice. Administration of recombinant LCN-2 to LCN-2-knockout mice restored inflammation to levels observed in wild-type mice. Neutralization of LCN-2 using a monoclonal antibody significantly reduced inflammation in wild-type mice. In contrast, LCN-2-knockout mice developed more severe serum-induced arthritis compared to wild-type mice. Histologic analysis revealed extensive tissue and bone destruction, with significantly reduced neutrophil infiltration but considerably more macrophage migration, in LCN-2-knockout mice compared to wild-type mice.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that LCN-2 may regulate immune cell recruitment to the site of inflammation, a process essential for the controlled initiation, perpetuation, and resolution of inflammatory processes. Thus, LCN-2 may present a promising target in the treatment of IC-mediated inflammatory/autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2013 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lipocalin-2 expressed in innate immune cells is an endogenous inhibitor of inflammation in murine nephrotoxic serum nephritis.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 4;8(7):e67693. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067693. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861783 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-10 regulate intramacrophage Chlamydia pneumoniae replication by modulating intracellular iron homeostasis.Immunobiology. 2013 Jul;218(7):969-78. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23317919 Free PMC article.
-
The pivotal role played by lipocalin-2 in chronic inflammatory pain.Exp Neurol. 2014 Apr;254:41-53. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Exp Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24440229
-
Adipocytokines and insulin resistance: the possible role of lipocalin-2, retinol binding protein-4, and adiponectin.Diabetes Care. 2009 Nov;32 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S362-7. doi: 10.2337/dc09-S340. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19875582 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Beyond fat mass: exploring the role of adipokines in rheumatic diseases.ScientificWorldJournal. 2011;11:1932-47. doi: 10.1100/2011/290142. Epub 2011 Oct 25. ScientificWorldJournal. 2011. PMID: 22194660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipocalin-2 Exacerbates Lupus Nephritis by Promoting Th1 Cell Differentiation.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Oct;31(10):2263-2277. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019090937. Epub 2020 Jul 9. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32646856 Free PMC article.
-
Lipocalin-2 deficiency may predispose to the progression of spontaneous age-related adiposity in mice.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 3;10(1):14589. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71249-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32883997 Free PMC article.
-
Mineralocorticoid Receptor and Aldosterone-Related Biomarkers of End-Organ Damage in Cardiometabolic Disease.Biomolecules. 2018 Sep 18;8(3):96. doi: 10.3390/biom8030096. Biomolecules. 2018. PMID: 30231508 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential of lipocalin-2/NGAL as biomarker for inflammatory and metabolic diseases.Biomarkers. 2015;20(8):565-71. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1123354. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Biomarkers. 2015. PMID: 26671823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exogenous Lipocalin 2 Ameliorates Acute Rejection in a Mouse Model of Renal Transplantation.Am J Transplant. 2016 Mar;16(3):808-20. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13521. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Am J Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26595644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Flower DR, North AC, Sansom CE. The lipocalin protein family: structural and sequence overview. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1482(1–2):9–24. - PubMed
-
- Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005;365(9466):1231–1238. - PubMed
-
- Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ, Holmes MA, Strong RK, et al. Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature. 2004;432(7019):917–921. - PubMed
-
- Devireddy LR, Gazin C, Zhu X, Green MR. A cell-surface receptor for lipocalin 24p3 selectively mediates apoptosis and iron uptake. Cell. 2005;123(7):1293–1305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

