The fibromyalgia family study: a genome-wide linkage scan study
- PMID: 23280346
- PMCID: PMC3618544
- DOI: 10.1002/art.37842
The fibromyalgia family study: a genome-wide linkage scan study
Abstract
Objective: Familial aggregation of fibromyalgia has been increasingly recognized. The goal of this study was to conduct a genome-wide linkage scan to identify susceptibility loci for fibromyalgia.
Methods: We genotyped members of 116 families from the Fibromyalgia Family Study and performed a model-free genome-wide linkage analysis of fibromyalgia with 341 microsatellite markers, using the Haseman-Elston regression approach.
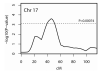
Results: The estimated sibling recurrence risk ratio (λs ) for fibromyalgia was 13.6 (95% confidence interval 10.0-18.5), based on a reported population prevalence of 2%. Genome-wide suggestive evidence of linkage was observed at markers D17S2196 (empirical P [Pe ]=0.00030) and D17S1294 (Pe=0.00035) on chromosome 17p11.2-q11.2.
Conclusion: The estimated sibling recurrence risk ratio (λs ) observed in this study suggests a strong genetic component of fibromyalgia. This is the first report of genome-wide suggestive linkage of fibromyalgia to the chromosome 17p11.2-q11.2 region. Further investigation of these multicase families from the Fibromyalgia Family Study is warranted to identify potential causal risk variants for fibromyalgia.
Copyright © 2013 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of fibromyalgia: report of the multicenter criteria committee. Arthritis Rheum. 1990;33:160–72. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe F, Ross K, Anderson J, Russell IJ, Hebert L. The prevalence and characteristics of fibromyalgia in the general population. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Russell IJ, Larson AA. Neurophysiopathogenesis of fibromyalgia syndrome: a unified hypothesis. Rheum Dis Clin Norht Am. 2009;35:421–35. - PubMed
-
- Henriksson KG. Fibromyalgia--from syndrome to disease. Overview of pathogenetic mechanisms. J Rehabil Med. 2003;41(Suppl):89–94. - PubMed
-
- Ablin J, Neumann L, Buskila D. Pathogenesis of fibromyalgia - a review. Joint Bone Spine. 2008 May;75:273–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

