Phylogenetic composition and distribution of picoeukaryotes in the hypoxic northwestern coast of the Gulf of Mexico
- PMID: 23281331
- PMCID: PMC3584219
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.57
Phylogenetic composition and distribution of picoeukaryotes in the hypoxic northwestern coast of the Gulf of Mexico
Abstract
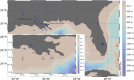
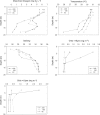
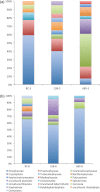
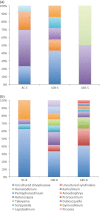
Coastal marine hypoxic, or low-oxygen, episodes are an increasing worldwide phenomenon, but its effect on the microbial community is virtually unknown by far. In this study, the community structure and phylogeny of picoeukaryotes in the Gulf of Mexico, which are exposed to severe hypoxia in these areas was explored through a clone library approach. Both oxic surface waters and suboxic bottom waters were collected in August 2010 from three representative stations on the inner Louisiana shelf near the Atchafalaya and Mississippi River plumes. The bottom waters of the two more western stations were much more hypoxic in comparison to those of the station closest to the Mississippi River plume, which were only moderately hypoxic. A phylogenetic analysis of a total 175 sequences, generated from six 18S rDNA clone libraries, demonstrated a clear dominance of parasitic dinoflagellates from Marine alveolate clades I and II in all hypoxic waters as well as in the surface layer at the more western station closest to the Atchafalaya River plume. Species diversity was significantly higher at the most hypoxic sites, and many novel species were present among the dinoflagellate and stramenopile clades. We concluded that hypoxia in the Gulf of Mexico causes a significant shift in picoeukaryote communities, and that hypoxia may cause a shift in microbial food webs from grazing to parasitism.
© 2012 The Authors. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. This is an open access article under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figures


References
-
- Arndt H. Functional diversity of heterotrophic flagellates in aquatic systems. In: Leadbeater BSC, Green JC, editors. The flagellates: unity, diversity and evolution. London, U.K: Taylor & Francis Press; 2000. pp. 240–268.
-
- Bass D, Cavalier-Smith T. Phylum-specific environmental DNA analysis reveals remarkably high global biodiversity of Cercozoa (Protozoa) Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004;54:2393–2404. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi TS, Cook RL, Perdue EM, Kolic PE, Green N, Zhang Y, et al. Impacts of diverted freshwater on dissolved organic matter and microbial communities in Barataria Bay, Louisiana, U.S.A. Mar. Environ. Res. 2011;72:248–257. - PubMed
-
- Boström KH, Simu K, Hagstrom Å, Riemann L. Optimization of DNA extraction for quantitative marine bacterioplankton community analysis. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods. 2004;2:365–373.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

