Regenerating new heart with stem cells
- PMID: 23281411
- PMCID: PMC3533279
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI63068
Regenerating new heart with stem cells
Retraction in
-
Regenerating new heart with stem cells.J Clin Invest. 2018 Dec 3;128(12):5676. doi: 10.1172/JCI126075. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30507606 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
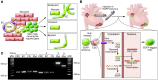
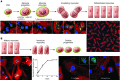
This article discusses current understanding of myocardial biology, emphasizing the regeneration potential of the adult human heart and the mechanisms involved. In the last decade, a novel conceptual view has emerged. The heart is no longer considered a postmitotic organ, but is viewed as a self-renewing organ characterized by a resident stem cell compartment responsible for tissue homeostasis and cardiac repair following injury. Additionally, HSCs possess the ability to transdifferentiate and acquire the cardiomyocyte, vascular endothelial, and smooth muscle cell lineages. Both cardiac and hematopoietic stem cells may be used therapeutically in an attempt to reverse the devastating consequences of chronic heart failure of ischemic and nonischemic origin.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG017042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG043353/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL114346/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL092868/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL078825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL091021/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL039902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105532/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026107/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL081737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

