TranSeqAnnotator: large-scale analysis of transcriptomic data
- PMID: 23282024
- PMCID: PMC3521237
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S17-S24
TranSeqAnnotator: large-scale analysis of transcriptomic data
Abstract
Background: The transcriptome of an organism can be studied with the analysis of expressed sequence tag (EST) data sets that offers a rapid and cost effective approach with several new and updated bioinformatics approaches and tools for assembly and annotation. The comprehensive analyses comprehend an organism along with the genome and proteome analysis. With the advent of large-scale sequencing projects and generation of sequence data at protein and cDNA levels, automated analysis pipeline is necessary to store, organize and annotate ESTs.
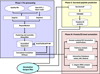
Results: TranSeqAnnotator is a workflow for large-scale analysis of transcriptomic data with the most appropriate bioinformatics tools for data management and analysis. The pipeline automatically cleans, clusters, assembles and generates consensus sequences, conceptually translates these into possible protein products and assigns putative function based on various DNA and protein similarity searches. Excretory/secretory (ES) proteins inferred from ESTs/short reads are also identified. The TranSeqAnnotator accepts FASTA format raw and quality ESTs along with protein and short read sequences and are analysed with user selected programs. After pre-processing and assembly, the dataset is annotated at the nucleotide, protein and ES protein levels.
Conclusion: TranSeqAnnotator has been developed in a Linux cluster, to perform an exhaustive and reliable analysis and provide detailed annotation. TranSeqAnnotator outputs gene ontologies, protein functional identifications in terms of mapping to protein domains and metabolic pathways. The pipeline is applied to annotate large EST datasets to identify several novel and known genes with therapeutic experimental validations and could serve as potential targets for parasite intervention. TransSeqAnnotator is freely available for the scientific community at http://estexplorer.biolinfo.org/TranSeqAnnotator/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ESTExplorer: an expressed sequence tag (EST) assembly and annotation platform.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W143-7. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm378. Epub 2007 Jun 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17545197 Free PMC article.
-
In silico analysis of expressed sequence tags from Trichostrongylus vitrinus (Nematoda): comparison of the automated ESTExplorer workflow platform with conventional database searches.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S1-S10. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18315841 Free PMC article.
-
An analysis of the transcriptome of Teladorsagia circumcincta: its biological and biotechnological implications.BMC Genomics. 2012;13 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-S7-S10. Epub 2012 Dec 13. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23282110 Free PMC article.
-
A hitchhiker's guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis.Brief Bioinform. 2007 Jan;8(1):6-21. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl015. Epub 2006 May 23. Brief Bioinform. 2007. PMID: 16772268 Review.
-
Tutorial: guidelines for annotating single-cell transcriptomic maps using automated and manual methods.Nat Protoc. 2021 Jun;16(6):2749-2764. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00534-0. Epub 2021 May 24. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34031612 Review.
Cited by
-
InCoB2012 Conference: from biological data to knowledge to technological breakthroughs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2012;13 Suppl 17(Suppl 17):S1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S17-S1. Epub 2012 Dec 13. BMC Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 23281929 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Supplementation in a Randomized Controlled Trial Decreased ZIP4 and ZIP8 mRNA Abundance in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Adult Women.Nutr Metab Insights. 2015 May 12;8:7-14. doi: 10.4137/NMI.S23233. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab Insights. 2015. PMID: 26023281 Free PMC article.
-
Macrogenomic Analysis Reveals Soil Microbial Diversity in Different Regions of the Antarctic Peninsula.Microorganisms. 2024 Nov 27;12(12):2444. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122444. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39770646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dong Q, Kroiss L, Oakley FD, Wang BB, Brendel V. Comparative EST analyses in plant systems. Methods Enzymol. 2005;395:400–418. - PubMed
-
- Moreno Y, Gros PP, Tam M, Segura M, Valanparambil R, Geary TG, Stevenson MM. Proteomic analysis of excretory-secretory products of Heligmosomoides polygyrus assessed with next-generation sequencing transcriptomic information. PLoS neglected tropical diseases. 2011;5(10):e1370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001370. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials