Prediction and analysis of protein solubility using a novel scoring card method with dipeptide composition
- PMID: 23282103
- PMCID: PMC3521471
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-13-S17-S3
Prediction and analysis of protein solubility using a novel scoring card method with dipeptide composition
Abstract
Background: Existing methods for predicting protein solubility on overexpression in Escherichia coli advance performance by using ensemble classifiers such as two-stage support vector machine (SVM) based classifiers and a number of feature types such as physicochemical properties, amino acid and dipeptide composition, accompanied with feature selection. It is desirable to develop a simple and easily interpretable method for predicting protein solubility, compared to existing complex SVM-based methods.
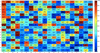
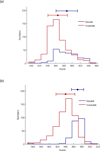
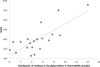
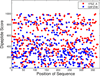
Results: This study proposes a novel scoring card method (SCM) by using dipeptide composition only to estimate solubility scores of sequences for predicting protein solubility. SCM calculates the propensities of 400 individual dipeptides to be soluble using statistic discrimination between soluble and insoluble proteins of a training data set. Consequently, the propensity scores of all dipeptides are further optimized using an intelligent genetic algorithm. The solubility score of a sequence is determined by the weighted sum of all propensity scores and dipeptide composition. To evaluate SCM by performance comparisons, four data sets with different sizes and variation degrees of experimental conditions were used. The results show that the simple method SCM with interpretable propensities of dipeptides has promising performance, compared with existing SVM-based ensemble methods with a number of feature types. Furthermore, the propensities of dipeptides and solubility scores of sequences can provide insights to protein solubility. For example, the analysis of dipeptide scores shows high propensity of α-helix structure and thermophilic proteins to be soluble.
Conclusions: The propensities of individual dipeptides to be soluble are varied for proteins under altered experimental conditions. For accurately predicting protein solubility using SCM, it is better to customize the score card of dipeptide propensities by using a training data set under the same specified experimental conditions. The proposed method SCM with solubility scores and dipeptide propensities can be easily applied to the protein function prediction problems that dipeptide composition features play an important role.
Availability: The used datasets, source codes of SCM, and supplementary files are available at http://iclab.life.nctu.edu.tw/SCM/.
Figures



References
-
- Idicula-Thomas S, Kulkarni AJ, Kulkarni BD, Jayaraman VK, Balaji PV. A support vector machine-based method for predicting the propensity of a protein to be soluble or to form inclusion body on overexpression in Escherichia coli. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(3):278–284. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti810. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jenkins TM, Hickman AB, Dyda F, Ghirlando R, Davies DR, Craigie R. Catalytic domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase: identification of a soluble mutant by systematic replacement of hydrophobic residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92(13):6057–6061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.6057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

