Desloratadine therapy improves allergic rhinitis symptoms in latin american children aged 6 to 12 years
- PMID: 23282979
- PMCID: PMC3650984
- DOI: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e31819cdfdb
Desloratadine therapy improves allergic rhinitis symptoms in latin american children aged 6 to 12 years
Abstract
Objective: : To determine the effectiveness of desloratadine syrup in relieving symptoms of allergic rhinitis (AR) among children in Latin America.
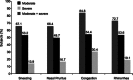
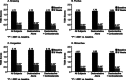
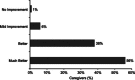
Methods: : In an open-label trial conducted in 5 Latin American countries, 455 children aged 6 to 12 years with seasonal or perennial AR were treated with desloratadine syrup 2.5 mg/d for 6 weeks. Thirty percent of subjects were concomitantly taking corticosteroids, and 21.3% had a history of asthma. Efficacy was measured by improvement in the Total Symptom Severity 4 questionnaire and decrease in severity of individual nasal symptoms of congestion, rhinorrhea, pruritus, and sneezing. Physicians and subjects' caregivers rated symptom improvement in a separate assessment at final visit.
Results: : Treatment with desloratadine led to a significant decrease in mean Total Symptom Severity 4 score, from 7.54 at baseline to 1.96 at study end (P < 0.0001), and in individual symptom scores, including congestion (P < 0.0001 for all). Similar improvements were found in groups receiving desloratadine monotherapy and desloratadine plus corticosteroids. Allergic rhinitis symptoms were rated "better" or "much better" by 94% of caregivers. Incidence of adverse events was 6%.
Conclusions: : Desloratadine, with or without concomitant corticosteroids, was efficacious and safe in the treatment of AR in this group of Latin American children.
Figures


References
-
- Richards W. Asthma, allergies, and school. Pediatr Ann. 1992;2:575–585. - PubMed
-
- Klein GL, Ziering RW, Girsh LS, Miller MF. The allergic irritability syndrome: four case reports and a position statement from the Neuroallergy Committee of the American College of Allergy. Ann Allergy. 1985;2:22–24. - PubMed
-
- Arrighi HM, Maier WC, Redding GJ, Morray BH, Llewellyn CE. The impact of allergic rhinitis in Seattle school children [Abstract 208] J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1995;2:192.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

