Interleukin-13 signaling and its role in asthma
- PMID: 23283176
- PMCID: PMC3651056
- DOI: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e31821188e0
Interleukin-13 signaling and its role in asthma
Abstract
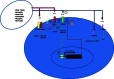
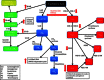
Asthma affects nearly 300 million people worldwide. The majority respond to inhaled corticosteroid treatment with or without beta-adrenergic agonists. However, a subset of 5 to 10% with severe asthma do not respond optimally to these medications. Different phenotypes of asthma may explain why current therapies show limited benefits in subgroups of patients. Interleukin-13 is implicated as a central regulator in IgE synthesis, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, and fibrosis. Promising research suggests that the interleukin-13 pathway may be an important target in the treatment of the different asthma phenotypes.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

