Current status and future prospects of epidemiology and public health training and research in the WHO African region
- PMID: 23283719
- PMCID: PMC3535755
- DOI: 10.1093/ije/dys189
Current status and future prospects of epidemiology and public health training and research in the WHO African region
Abstract
Background: To date little has been published about epidemiology and public health capacity (training, research, funding, human resources) in WHO/AFRO to help guide future planning by various stakeholders.
Methods: A bibliometric analysis was performed to identify published epidemiological research. Information about epidemiology and public health training, current research and challenges was collected from key informants using a standardized questionnaire.
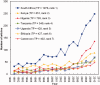
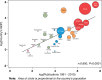
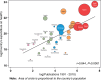
Results: From 1991 to 2010, epidemiology and public health research output in the WHO/AFRO region increased from 172 to 1086 peer-reviewed articles per annum [annual percentage change (APC) = 10.1%, P for trend < 0.001]. The most common topics were HIV/AIDS (11.3%), malaria (8.6%) and tuberculosis (7.1%). Similarly, numbers of first authors (APC = 7.3%, P for trend < 0.001), corresponding authors (APC = 8.4%, P for trend < 0.001) and last authors (APC = 8.5%, P for trend < 0.001) from Africa increased during the same period. However, an overwhelming majority of respondents (>90%) reported that this increase is only rarely linked to regional post-graduate training programmes in epidemiology. South Africa leads in publications (1978/8835, 22.4%), followed by Kenya (851/8835, 9.6%), Nigeria (758/8835, 8.6%), Tanzania (549/8835, 6.2%) and Uganda (428/8835, 4.8%) (P < 0.001, each vs South Africa). Independent predictors of relevant research productivity were 'in-country numbers of epidemiology or public health programmes' [incidence rate ratio (IRR) = 3.41; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.90-6.11; P = 0.03] and 'number of HIV/AIDS patients' (IRR = 1.30; 95% CI 1.02-1.66; P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Since 1991, there has been increasing epidemiological research productivity in WHO/AFRO that is associated with the number of epidemiology programmes and burden of HIV/AIDS cases. More capacity building and training initiatives in epidemiology are required to promote research and address the public health challenges facing the continent.
Figures



Comment in
-
Epidemiology and public health research productivity in Africa.Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Jun;42(3):913. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt050. Epub 2013 May 6. Int J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23649187 No abstract available.
-
Authors' response to: Epidemiology and public health research productivity in Africa.Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Jun;42(3):913-4. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt051. Epub 2013 May 6. Int J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 23649188 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Current status and future prospects of epidemiology and public health training and research in the WHO African region.Int J Epidemiol. 2013 Oct;42(5):1522-3. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyt099. Int J Epidemiol. 2013. PMID: 24159081 No abstract available.
References
-
- Porta M. A Dictionary of Epidemiology. 5th edn. Oxford University Press; 2008.
-
- Greysen SR, Dovlo D, Olapade-Olaopa EO, Jacobs M, Sewankambo N, Mullan F. Medical education in sub-Saharan Africa: a literature review. Med Educ. 2011;45:973–86. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Risks: Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2009. http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/risk_factors/en/inde... (26 June 2011, date last accessed)
-
- Ezzati M, Lopez A, Rodgers A, et al. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet. 2002;360:1347–60. - PubMed

