Recruitment of histone methyltransferase G9a mediates transcriptional repression of Fgf21 gene by E4BP4 protein
- PMID: 23283977
- PMCID: PMC3581381
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433482
Recruitment of histone methyltransferase G9a mediates transcriptional repression of Fgf21 gene by E4BP4 protein
Abstract
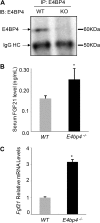
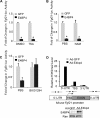
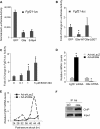
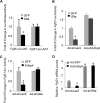
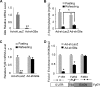
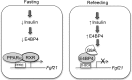
The liver responds to fasting-refeeding cycles by reprogramming expression of metabolic genes. Fasting potently induces one of the key hepatic hormones, fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), to promote lipolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and ketogenesis, whereas refeeding suppresses its expression. We previously reported that the basic leucine zipper transcription factor E4BP4 (E4 binding protein 4) represses Fgf21 expression and disrupts its circadian oscillations in cultured hepatocytes. However, the epigenetic mechanism for E4BP4-dependent suppression of Fgf21 has not yet been addressed. Here we present evidence that histone methyltransferase G9a mediates E4BP4-dependent repression of Fgf21 during refeeding by promoting repressive histone modification. We find that Fgf21 expression is up-regulated in E4bp4 knock-out mouse liver. We demonstrate that the G9a-specific inhibitor BIX01294 abolishes suppression of the Fgf21 promoter activity by E4BP4, whereas overexpression of E4bp4 leads to increased levels of dimethylation of histone 3 lysine 9 (H3K9me2) around the Fgf21 promoter region. Furthermore, we also show that E4BP4 interacts with G9a, and knockdown of G9a blocks repression of Fgf21 promoter activity and expression in cells overexpressing E4bp4. A G9a mutant lacking catalytic activity, due to deletion of the SET domain, fails to inhibit the Fgf21 promoter activity. Importantly, acute hepatic knockdown by adenoviral shRNA targeting G9a abolishes Fgf21 repression by refeeding, concomitant with decreased levels of H3K9me2 around the Fgf21 promoter region. In summary, we show that G9a mediates E4BP4-dependent suppression of hepatic Fgf21 by enhancing histone methylation (H3K9me2) of the Fgf21 promoter.
Figures

References
-
- Badman M. K., Pissios P., Kennedy A. R., Koukos G., Flier J. S., Maratos-Flier E. (2007) Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARα and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 5, 426–437 - PubMed
-
- Inagaki T., Dutchak P., Zhao G., Ding X., Gautron L., Parameswara V., Li Y., Goetz R., Mohammadi M., Esser V., Elmquist J. K., Gerard R. D., Burgess S. C., Hammer R. E., Mangelsdorf D. J., Kliewer S. A. (2007) Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARα-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 5, 415–425 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

