Mitochondrial protein import: Mia40 facilitates Tim22 translocation into the inner membrane of mitochondria
- PMID: 23283984
- PMCID: PMC3583659
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-09-0649
Mitochondrial protein import: Mia40 facilitates Tim22 translocation into the inner membrane of mitochondria
Abstract
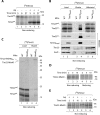
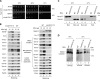
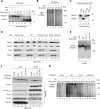
The mitochondrial intermembrane space assembly (MIA) pathway is generally considered to be dedicated to the redox-dependent import and biogenesis of proteins localized to the intermembrane space of mitochondria. The oxidoreductase Mia40 is a central component of the pathway responsible for the transfer of disulfide bonds to intermembrane space precursor proteins, causing their oxidative folding. Here we present the first evidence that the function of Mia40 is not restricted to the transport and oxidative folding of intermembrane space proteins. We identify Tim22, a multispanning membrane protein and core component of the TIM22 translocase of inner membrane, as a protein with cysteine residues undergoing oxidation during Tim22 biogenesis. We show that Mia40 is involved in the biogenesis and complex assembly of Tim22. Tim22 forms a disulfide-bonded intermediate with Mia40 upon import into mitochondria. Of interest, Mia40 binds the Tim22 precursor also via noncovalent interactions. We propose that Mia40 not only is responsible for disulfide bond formation, but also assists the Tim22 protein in its integration into the inner membrane of mitochondria.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and functional roles of the conserved cysteine residues of the redox-regulated import receptor Mia40 in the intermembrane space of mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2009 Jan 16;284(3):1353-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805035200. Epub 2008 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19011240
-
Mitochondrial Ccs1 contains a structural disulfide bond crucial for the import of this unconventional substrate by the disulfide relay system.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Oct;22(20):3758-67. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0296. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21865601 Free PMC article.
-
Mia40-dependent oxidation of cysteines in domain I of Ccs1 controls its distribution between mitochondria and the cytosol.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Oct;22(20):3749-57. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0293. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21865594 Free PMC article.
-
A disulfide relay system in mitochondria.Cell. 2005 Jul 1;121(7):965-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.019. Cell. 2005. PMID: 15989945 Review.
-
Structural basis for the disulfide relay system in the mitochondrial intermembrane space.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010 Nov 1;13(9):1359-73. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3099. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2010. PMID: 20136511 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of the Tim17 protein family.Biol Direct. 2016 Oct 19;11(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s13062-016-0157-y. Biol Direct. 2016. PMID: 27760563 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial protein import: An unexpected disulfide bond.J Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 15;214(4):363-5. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201607117. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27502488 Free PMC article.
-
Augmenter of liver regeneration regulates cellular iron homeostasis by modulating mitochondrial transport of ATP-binding cassette B8.Elife. 2021 Apr 9;10:e65158. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65158. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33835027 Free PMC article.
-
A disulfide bond in the TIM23 complex is crucial for voltage gating and mitochondrial protein import.J Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 15;214(4):417-31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201602074. Epub 2016 Aug 8. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27502485 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Translocation into the Intermembrane Space and Matrix of Mitochondria: Mechanisms and Driving Forces.Front Mol Biosci. 2017 Dec 7;4:83. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00083. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 29270408 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Banci L, Bertini I, Cefaro C, Ciofi-Baffoni S, Gallo A, Martinelli M, Sideris DP, Katrakili N, Tokatlidis K. MIA40 is an oxidoreductase that catalyzes oxidative protein folding in mitochondria. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:198–206. - PubMed
-
- Becker T, Böttinger L, Pfanner N. Mitochondrial protein import: from transport pathways to an integrated network. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012;37:85–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

