Necrotic renal epithelial cell inhibits renal interstitial fibroblast activation: role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- PMID: 23283996
- PMCID: PMC3602703
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00564.2012
Necrotic renal epithelial cell inhibits renal interstitial fibroblast activation: role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
Abstract
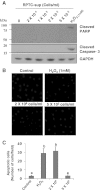
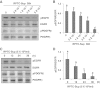
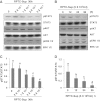
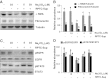
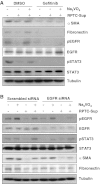
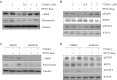
Our recent studies showed that contents of necrotic renal proximal tubular cells (RPTC) from 2 × 10(6) cells/ml directly induced death of cultured renal interstitial fibroblasts. However, it remains unknown whether nonlethal number of necrotic RPTC would also alter the fate of renal interstitial fibroblasts. To address this issue, renal interstitial fibroblasts (NRK-49F) were exposed to necrotic RPTC supernatant (RPTC-Sup) obtained from 2 × 10(4) to 5 × 10(5) cells/ml. These concentrations of RPTC did not induce cell death, but led to inactivation of renal fibroblasts as indicated by reduced expression of α-smooth muscle actin and fibronectin, two hallmarks of activated fibroblasts. Concurrently, the same doses of necrotic RPTC-Sup suppressed phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 (STAT3) in a time- and dose-dependent manner, but did not affect phosphorylation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β, AKT, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. The presence of sodium orthovanadate, a general protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) inhibitor or TCS-401 (a selective PTP1B inhibitor), abrogated those effects of RPTC-Sup, whereas coincubation with the EGFR inhibitor (Gefitinib) or silencing of EGFR with siRNA preserved the ability of RPTC-Sup in suppressing renal fibroblast activation and STAT3 phosphorylation. Moreover, RPTC-Sup treatment induced PTP1B phosphorylation and its interaction with EGFR. Collectively, these results indicate that nonlethal necrotic RPTC-Sup can induce inactivation of renal interstitial fibroblasts, which occurs through a mechanism involved in PTP1B-mediated inhibition of EGFR signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
ERK pathway mediates P2X7 expression and cell death in renal interstitial fibroblasts exposed to necrotic renal epithelial cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):F650-9. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00215.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 15. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21677150 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy protects against necrotic renal epithelial cell-induced death of renal interstitial fibroblasts.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Jul 1;303(1):F83-91. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00027.2012. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22496408 Free PMC article.
-
P2X7 receptors mediate deleterious renal epithelial-fibroblast cross talk.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Jan;300(1):F62-70. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00473.2010. Epub 2010 Sep 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 20861083 Free PMC article.
-
Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in acute and chronic kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2013 May;83(5):804-10. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.435. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23325080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of renal cell repair and regeneration after acute renal failure.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Mar;304(3):905-12. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.035022. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12604664 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Sirtuin-1 Promotes Renal Fibroblast Activation and Aggravates Renal Fibrogenesis.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Aug;354(2):142-51. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.224386. Epub 2015 May 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 26022003 Free PMC article.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases: from mechanisms to therapeutics.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Aug 22;11:1445739. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1445739. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39238503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR/ErbB) for the potential treatment of renal pathologies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1394997. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1394997. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39234105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications.J Physiol Biochem. 2022 May;78(2):307-322. doi: 10.1007/s13105-021-00860-7. Epub 2022 Jan 6. J Physiol Biochem. 2022. PMID: 34988903 Review.
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B regulates migration of ARPE-19 cells through EGFR/ERK signaling pathway.Int J Ophthalmol. 2015 Oct 18;8(5):891-7. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2015.05.07. eCollection 2015. Int J Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 26558197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asada N, Takase M, Nakamura J, Oguchi A, Asada M, Suzuki N, Yamamura K, Nagoshi N, Shibata S, Rao TN, Fehling HJ, Fukatsu A, Minegishi N, Kita T, Kimura T, Okano H, Yamamoto M, Yanagita M. Dysfunction of fibroblasts of extrarenal origin underlies renal fibrosis and renal anemia in mice. J Clin Invest 121: 3981–3990, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmann S, Le Hir M, Eckardt KU. Co-localization of erythropoietin mRNA and ecto-5′-nucleotidase immunoreactivity in peritubular cells of rat renal cortex indicates that fibroblasts produce erythropoietin. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 335–341, 1993 - PubMed
-
- Bonner JC. Regulation of PDGF and its receptors in fibrotic diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15: 255–273, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Bourdeau A, Dube N, Tremblay ML. Cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatases, regulation and function: the roles of PTP1B and TC-PTP. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 203–209, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Ceacareanu B, Zhuang D, Zhang C, Pu Q, Ceacareanu AC, Hassid A. Counterregulatory function of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B in platelet-derived growth factor- or fibroblast growth factor-induced motility and proliferation of cultured smooth muscle cells and in neointima formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26: 501–507, 2006 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

