Endoreplication
- PMID: 23284048
- PMCID: PMC3579398
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a012948
Endoreplication
Abstract
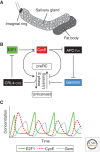
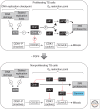
Developmentally programmed polyploidy occurs by at least four different mechanisms, two of which (endoreduplication and endomitosis) involve switching from mitotic cell cycles to endocycles by the selective loss of mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) activity and bypassing many of the processes of mitosis. Here we review the mechanisms of endoreplication, focusing on recent results from Drosophila and mice.
Figures


References
-
- Arias EE, Walter JC 2006. PCNA functions as a molecular platform to trigger Cdt1 destruction and prevent re-replication. Nat Cell Biol 8: 84–90 - PubMed
-
- Audibert A, Simon F, Gho M 2005. Cell cycle diversity involves differential regulation of Cyclin E activity in the Drosophila bristle cell lineage. Development 132: 2287–2297 - PubMed
-
- Besson A, Dowdy SF, Roberts JM 2008. CDK inhibitors: Cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell 14: 159–169 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
