Elevated plasma angiopoietin-2 levels and primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation
- PMID: 23284823
- PMCID: PMC3526525
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051932
Elevated plasma angiopoietin-2 levels and primary graft dysfunction after lung transplantation
Abstract
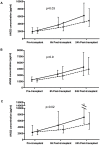
Introduction: Primary graft dysfunction (PGD) is a significant contributor to early morbidity and mortality after lung transplantation. Increased vascular permeability in the allograft has been identified as a possible mechanism leading to PGD. Angiopoietin-2 serves as a partial antagonist to the Tie-2 receptor and induces increased endothelial permeability. We hypothesized that elevated Ang2 levels would be associated with development of PGD.
Methods: We performed a case-control study, nested within the multi-center Lung Transplant Outcomes Group cohort. Plasma angiopoietin-2 levels were measured pre-transplant and 6 and 24 hours post-reperfusion. The primary outcome was development of grade 3 PGD in the first 72 hours. The association of angiopoietin-2 plasma levels and PGD was evaluated using generalized estimating equations (GEE).
Results: There were 40 PGD subjects and 79 non-PGD subjects included for analysis. Twenty-four PGD subjects (40%) and 47 non-PGD subjects (59%) received a transplant for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Among all subjects, GEE modeling identified a significant change in angiopoietin-2 level over time in cases compared to controls (p = 0.03). The association between change in angiopoietin-2 level over the perioperative time period was most significant in patients with a pre-operative diagnosis of IPF (p = 0.02); there was no statistically significant correlation between angiopoietin-2 plasma levels and the development of PGD in the subset of patients transplanted for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (p = 0.9).
Conclusions: Angiopoietin-2 levels were significantly associated with the development of PGD after lung transplantation. Further studies examining the regulation of endothelial cell permeability in the pathogenesis of PGD are indicated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Arcasoy SM, Fisher A, Hachem RR, Scavuzzo M, Ware LB (2005) Report of the ISHLT Working Group on Primary Lung Graft Dysfunction part V: predictors and outcomes. J Heart Lung Transplant 24: 1483–8. - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Bavaria JE, Palevsky HI, Litzky L, Blumenthal N, et al. (1998) Primary Graft Failure Following Lung Transplantation. Chest 114: 51–60. - PubMed
-
- Christie JD, Kotloff RM, Pochettino A, Arcasoy SM, Rosengard BR, et al. (2003) Clinical risk factors for primary graft failure following lung transplantation. Chest 124: 1232–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

