Trends in overweight and obesity among children and adolescents in China from 1981 to 2010: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 23284829
- PMCID: PMC3524084
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051949
Trends in overweight and obesity among children and adolescents in China from 1981 to 2010: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Overweight/obesity is a serious public health problem that affects a large part of the world population across all age and racial/ethnic groups. However, there has not been a meta-analysis of the prevalence of childhood and adolescent overweight/obesity in China during the past 30 years.
Methods: The China National Knowledge Infrastructure and Wanfang DATA, MEDLINE, EMBASE and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature were searched for relevant studies published between January 1970 and June 2012. The prevalence of overweight/obesity over time was pooled using Stata/SE, version 9. Summary statistics (odds ratios, ORs) were used to compare sex-specific and urban-rural preponderance of overweight/obesity using Review Manager.
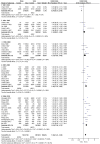
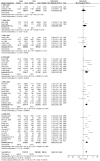
Results: After screening 1326 papers, we included 35 papers (41 studies), most of medium quality. The prevalence of overweight/obesity increased from 1.8% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.4%-3.1%) and 0.4% (95% CI, -0.1% to -0.8%) respectively in 1981-1985 to 13.1% (95% CI, 11.2%-15.0%) and 7.5% (95% CI, 6.6%-8.4%) respectively in 2006-2010. The average annual increase was 8.3% and 12.4% respectively. Boys were more likely to be overweight/obese than girls (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.24-1.49 and OR, 1.68; 95% CI, 1.52-1.86 respectively). The prevalence of overweight/obesity was higher in urban areas than in rural areas (OR, 1.66; 95% CI, 1.54-1.79 and OR, 1.97; 95% CI, 1.68-2.30 respectively). For age-specific subgroup analyses, both overweight and obesity increased more rapidly in the toddler stage than in other developmental stages. Sensitivity analyses showed that sample-size differences, study quality, overweight/obesity criteria and geographical distribution affected overweight/obesity prevalence.
Conclusions: Toddlers and urban boys were at particularly high risk; the prevalence in these groups increased more rapidly than in their counterparts. Public health prevention strategies are urgently needed to modify health behaviors of children and adolescents and control overweight/obesity in China.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zhao W, Zhai Y, Hu J, Wang J, Yang Z, et al. (2008) Economic burden of obesity-related chronic diseases in mainland China. Obes Rev 9: 62–67. - PubMed
-
- Yu ZB, Han SP, Cao XG, Guo XR (2010) Intelligence in relation to obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev 11: 656–670. - PubMed
-
- Vander WJS, Mitchell ER (2011) Psychological complications of pediatric obesity. Pediatr Clin North Am 58: 1393–1401. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed ML, Ong KK, Dunger DB (2009) Childhood obesity and the timing of puberty. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20: 237–242. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous