A new class of wheat gliadin genes and proteins
- PMID: 23284903
- PMCID: PMC3527421
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052139
A new class of wheat gliadin genes and proteins
Abstract
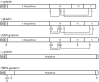
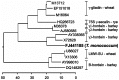
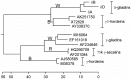
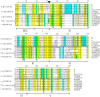
The utility of mining DNA sequence data to understand the structure and expression of cereal prolamin genes is demonstrated by the identification of a new class of wheat prolamins. This previously unrecognized wheat prolamin class, given the name δ-gliadins, is the most direct ortholog of barley γ3-hordeins. Phylogenetic analysis shows that the orthologous δ-gliadins and γ3-hordeins form a distinct prolamin branch that existed separate from the γ-gliadins and γ-hordeins in an ancestral Triticeae prior to the branching of wheat and barley. The expressed δ-gliadins are encoded by a single gene in each of the hexaploid wheat genomes. This single δ-gliadin/γ3-hordein ortholog may be a general feature of the Triticeae tribe since examination of ESTs from three barley cultivars also confirms a single γ3-hordein gene. Analysis of ESTs and cDNAs shows that the genes are expressed in at least five hexaploid wheat cultivars in addition to diploids Triticum monococcum and Aegilops tauschii. The latter two sequences also allow assignment of the δ-gliadin genes to the A and D genomes, respectively, with the third sequence type assumed to be from the B genome. Two wheat cultivars for which there are sufficient ESTs show different patterns of expression, i.e., with cv Chinese Spring expressing the genes from the A and B genomes, while cv Recital has ESTs from the A and D genomes. Genomic sequences of Chinese Spring show that the D genome gene is inactivated by tandem premature stop codons. A fourth δ-gliadin sequence occurs in the D genome of both Chinese Spring and Ae. tauschii, but no ESTs match this sequence and limited genomic sequences indicates a pseudogene containing frame shifts and premature stop codons. Sequencing of BACs covering a 3 Mb region from Ae. tauschii locates the δ-gliadin gene to the complex Gli-1 plus Glu-3 region on chromosome 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The gene space in wheat: the complete γ-gliadin gene family from the wheat cultivar Chinese Spring.Funct Integr Genomics. 2013 Jun;13(2):261-73. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0321-8. Epub 2013 Apr 7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23564033
-
New insights into structural organization and gene duplication in a 1.75-Mb genomic region harboring the α-gliadin gene family in Aegilops tauschii, the source of wheat D genome.Plant J. 2017 Nov;92(4):571-583. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13675. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Plant J. 2017. PMID: 28857322
-
Molecular characterization of the celiac disease epitope domains in α-gliadin genes in Aegilops tauschii and hexaploid wheats (Triticum aestivum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2010 Nov;121(7):1239-51. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1384-8. Epub 2010 Jun 17. Theor Appl Genet. 2010. PMID: 20556595
-
Genome-wide identification, characteristics and expression of the prolamin genes in Thinopyrum elongatum.BMC Genomics. 2021 Dec 2;22(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08088-x. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34852761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Biochemical and molecular characterization of gliadins].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006 Sep-Oct;40(5):796-807. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2006. PMID: 17086980 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
What Is Gluten-Why Is It Special?Front Nutr. 2019 Jul 5;6:101. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00101. eCollection 2019. Front Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31334243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heteroalleles in Common Wheat: Multiple Differences between Allelic Variants of the Gli-B1 Locus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 12;22(4):1832. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041832. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33673225 Free PMC article.
-
A ddRADseq Survey of the Genetic Diversity of Rye (Secale cereale L.) Landraces from the Western Alps Reveals the Progressive Reduction of the Local Gene Pool.Plants (Basel). 2021 Nov 9;10(11):2415. doi: 10.3390/plants10112415. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34834778 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the celiac disease-related immunogenic complexes in a set of wheat and tritordeum genotypes: implications for low-gluten precision breeding in cereal crops.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 11;14:1171882. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1171882. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37251754 Free PMC article.
-
Towards reducing the immunogenic potential of wheat flour: omega gliadins encoded by the D genome of hexaploid wheat may also harbor epitopes for the serious food allergy WDEIA.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Nov 21;18(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1506-z. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30463509 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shewry PR, Halford NG, Lafiandra D (2003) Genetics of wheat gluten proteins. Adv Genet 49: 111–184. - PubMed
-
- Sabelli PA, Shewry PR (1991) Characterization and organization of gene families at the Gli-1 loci of bread and durum wheats by restriction fragment analysis. Theor Appl Genet 83: 209–227. - PubMed
-
- Shewry PR, Kreis M, Parmar S, Lew EJ-L, Kasarda DD (1985) Identification of gamma-type hordeins in barley. FEBS Let 190: 61–64.
-
- Rechinger KB, Bougri OV, Cameron-Mills V (1993) Evolutionary relationship of the members of the sulphur-rich hordein family revealed by common antigenic determinants. Theor Appl Genet 85: 829–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

