Transport mechanisms and their pathology-induced regulation govern tyrosine kinase inhibitor delivery in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 23284953
- PMCID: PMC3527388
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052247
Transport mechanisms and their pathology-induced regulation govern tyrosine kinase inhibitor delivery in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are effective in treating malignant disorders and were lately suggested to have an impact on non-malignant diseases. However, in some inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA) the in vivo effect seemed to be moderate. As most TKIs are taken up actively into cells by cell membrane transporters, this study aimed to evaluate the role of such transporters for the accumulation of the TKI Imatinib mesylates in RA synovial fibroblasts as well as their regulation under inflammatory conditions.
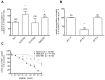
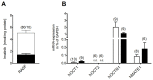
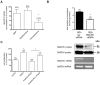
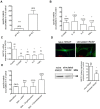
Methodology/principal findings: The transport and accumulation of Imatinib was investigated in transporter-transfected HEK293 cells and human RA synovial fibroblasts (hRASF). Transporter expression was quantified by qRT-PCR. In transfection experiments, hMATE1 showed the highest apparent affinity for Imatinib among all known Imatinib transporters. Experiments quantifying the Imatinib uptake in the presence of specific transporter inhibitors and after siRNA knockdown of hMATE1 indeed identified hMATE1 to mediate Imatinib transport in hRASF. The anti-proliferative effect of Imatinib on PDGF stimulated hRASF was quantified by cell counting and directly correlated with the uptake activity of hMATE1. Expression of hMATE1 was investigated by Western blot and immuno-fluorescence. Imatinib transport under disease-relevant conditions, such as an altered pH and following stimulation with different cytokines, was also investigated by HPLC. The uptake was significantly reduced by an acidic extracellular pH as well as by the cytokines TNFα, IL-1β and IL-6, which all decreased the expression of hMATE1-mRNA and protein.
Conclusion/significance: The regulation of Imatinib uptake via hMATE1 in hRASF and resulting effects on their proliferation may explain moderate in vivo effects on RA. Moreover, our results suggest that investigating transporter mediated drug processing under normal and pathological conditions is important for developing intracellular acting drugs used in inflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Importance of the novel organic cation transporter 1 for tyrosine kinase inhibition by saracatinib in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 28;7(1):1258. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01438-4. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28455521 Free PMC article.
-
Imatinib mesylate inhibits proliferation of rheumatoid synovial fibroblast-like cells and phosphorylation of Gab adapter proteins activated by platelet-derived growth factor.Clin Exp Immunol. 2006 May;144(2):335-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2006.03067.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16634808 Free PMC article.
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib effectively blocks PDGF-induced orbital fibroblast activation.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014 Jul;252(7):1101-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-014-2674-7. Epub 2014 May 30. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014. PMID: 24874745
-
Interaction of tyrosine kinase inhibitors with the human multidrug transporter proteins, MDR1 and MRP1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002 Jul 18;1587(2-3):318-25. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4439(02)00095-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002. PMID: 12084474 Review.
-
Imatinib mesylate: an innovation in treatment of autoimmune diseases.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2013 Sep;7(3):259-67. doi: 10.2174/1872213x113079990021. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23947692 Review.
Cited by
-
Solute carrier nutrient transporters in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 20;13:984408. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.984408. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36341411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the plasma membrane transporter of organic cations OCT1 and its genetic variants in modern liver pharmacology.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:692071. doi: 10.1155/2013/692071. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23984399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interaction of Masitinib with Organic Cation Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 16;23(22):14189. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214189. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430667 Free PMC article.
-
Tofacitinib and Baricitinib Are Taken up by Different Uptake Mechanisms Determining the Efficacy of Both Drugs in RA.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 10;21(18):6632. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186632. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32927842 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of MATE1, P-gp, OCTN1 and OCTN2, in epithelial and immune cells in the lung of COPD and healthy individuals.Respir Res. 2018 Apr 20;19(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0760-9. Respir Res. 2018. PMID: 29678179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grimminger F, Schermuly RT, Ghofrani HA (2010) Targeting non-malignant disorders with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9: 956–970. - PubMed
-
- Distler JH, Distler O (2010) Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the treatment of fibrotic diseases such as systemic sclerosis: towards molecular targeted therapies. Ann Rheum Dis 69 Suppl 1i48–i51. - PubMed
-
- Paniagua RT, Robinson WH (2007) Imatinib for the treatment of rheumatic diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3: 190–191. - PubMed
-
- Akashi N, Matsumoto I, Tanaka Y, Inoue A, Yamamoto K, et al. (2011) Comparative suppressive effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors imatinib and nilotinib in models of autoimmune arthritis. Mod Rheumatol 21: 267–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

