Axonal synapses utilize multiple synaptic ribbons in the mammalian retina
- PMID: 23284975
- PMCID: PMC3524110
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052295
Axonal synapses utilize multiple synaptic ribbons in the mammalian retina
Abstract
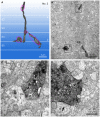
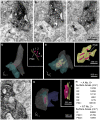
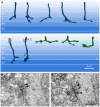
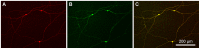
In the mammalian retina, bipolar cells and ganglion cells which stratify in sublamina a of the inner plexiform layer (IPL) show OFF responses to light stimuli while those that stratify in sublamina b show ON responses. This functional relationship between anatomy and physiology is a key principle of retinal organization. However, there are at least three types of retinal neurons, including intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells (ipRGCs) and dopaminergic amacrine cells, which violate this principle. These cell types have light-driven ON responses, but their dendrites mainly stratify in sublamina a of the IPL, the OFF sublayer. Recent anatomical studies suggested that certain ON cone bipolar cells make axonal or ectopic synapses as they descend through sublamina a, thus providing ON input to cells which stratify in the OFF sublayer. Using immunoelectron microscopy with 3-dimensional reconstruction, we have identified axonal synapses of ON cone bipolar cells in the rabbit retina. Ten calbindin ON cone bipolar axons made en passant ribbon synapses onto amacrine or ganglion dendrites in sublamina a of the IPL. Compared to the ribbon synapses made by bipolar terminals, these axonal ribbon synapses were characterized by a broad postsynaptic element that appeared as a monad and by the presence of multiple short synaptic ribbons. These findings confirm that certain ON cone bipolar cells can provide ON input to amacrine and ganglion cells whose dendrites stratify in the OFF sublayer via axonal synapses. The monadic synapse with multiple ribbons may be a diagnostic feature of the ON cone bipolar axonal synapse in sublamina a. The presence of multiple ribbons and a broad postsynaptic density suggest these structures may be very efficient synapses. We also identified axonal inputs to ipRGCs with the architecture described above.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ectopic retinal ON bipolar cell synapses in the OFF inner plexiform layer: contacts with dopaminergic amacrine cells and melanopsin ganglion cells.J Comp Neurol. 2009 Nov 10;517(2):226-44. doi: 10.1002/cne.22158. J Comp Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19731338 Free PMC article.
-
ON inputs to the OFF layer: bipolar cells that break the stratification rules of the retina.J Neurosci. 2009 Jul 15;29(28):8875-83. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0912-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19605625 Free PMC article.
-
ON cone bipolar cell axonal synapses in the OFF inner plexiform layer of the rabbit retina.J Comp Neurol. 2013 Apr 1;521(5):977-1000. doi: 10.1002/cne.23244. J Comp Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23042441 Free PMC article.
-
Development of On and Off retinal pathways and retinogeniculate projections.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004 Jan;23(1):31-51. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2003.10.001. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2004. PMID: 14766316 Review.
-
Bipolar Cell Pathways in the Vertebrate Retina.2007 May 24 [updated 2012 Jan 20]. In: Kolb H, Fernandez E, Jones B, Nelson R, editors. Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System [Internet]. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center; 1995–. 2007 May 24 [updated 2012 Jan 20]. In: Kolb H, Fernandez E, Jones B, Nelson R, editors. Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System [Internet]. Salt Lake City (UT): University of Utah Health Sciences Center; 1995–. PMID: 21413382 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations of the synapse of the inner retinal layers after chronic intraocular pressure elevation in glaucoma animal model.Mol Brain. 2014 Aug 13;7:53. doi: 10.1186/s13041-014-0053-2. Mol Brain. 2014. PMID: 25116810 Free PMC article.
-
The M6 cell: A small-field bistratified photosensitive retinal ganglion cell.J Comp Neurol. 2019 Jan 1;527(1):297-311. doi: 10.1002/cne.24556. Epub 2018 Nov 11. J Comp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30311650 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Circadian Phototransduction: Retinal Neurophysiology and Neuroanatomy.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 5;14:615305. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.615305. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33613175 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of Mouse Retinal Bipolar Cells: Type-Specific Connectivity with Special Reference to Rod-Driven AII Amacrine Pathways.Front Neuroanat. 2017 Oct 24;11:92. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2017.00092. eCollection 2017. Front Neuroanat. 2017. PMID: 29114208 Free PMC article.
-
A Color Vision Circuit for Non-Image-Forming Vision in the Primate Retina.Curr Biol. 2020 Apr 6;30(7):1269-1274.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.01.040. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Curr Biol. 2020. PMID: 32084404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nelson R, Kolb H (1983) Synaptic patterns and response properties of bipolar and ganglion cells in the cat retina. Vision Res 23: 1183–1195. - PubMed
-
- Sterling P, Smith R, Rao R, Vardi N (1995) Functional architecture of mammalian outer retina and bipolar cells.; Archer S DM, Vallerga S, editor. London: Chapman & Hall.
-
- Boycott B, Wässle H (1999) Parallel processing in the mammalian retina: the Proctor Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40: 1313–1327. - PubMed
-
- Wässle H (2004) Parallel processing in the mammalian retina. Nat Rev Neurosci 5: 747–757. - PubMed
-
- Boycott BB, Wässle H (1991) Morphological Classification of Bipolar Cells of the Primate Retina. Eur J Neurosci 3: 1069–1088. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

