The h-current in the substantia Nigra pars compacta neurons: a re-examination
- PMID: 23284989
- PMCID: PMC3528748
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052329
The h-current in the substantia Nigra pars compacta neurons: a re-examination
Abstract
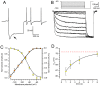
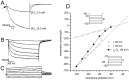
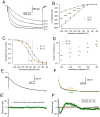
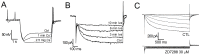
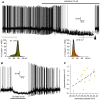
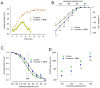
The properties of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (I(h)) were investigated in rat substantia nigra - pars compacta (SNc) principal neurons using patch-clamp recordings in thin slices. A reliable identification of single dopaminergic neurons was made possible by the use of a transgenic line of mice expressing eGFP under the tyrosine hydroxylase promoter. The effects of temperature and different protocols on the I(h) kinetics showed that, at 37°C and minimizing the disturbance of the intracellular milieu with perforated patch, this current actually activates at potentials more positive than what is generally indicated, with a half-activation potential of -77.05 mV and with a significant level of opening already at rest, thereby substantially contributing to the control of membrane potential, and ultimately playing a relevant function in the regulation of the cell excitability. The implications of the known influence of intracellular cAMP levels on I(h) amplitude and kinetics were examined. The direct application of neurotransmitters (DA, 5-HT and noradrenaline) physiologically released onto SNc neurons and known to act on metabotropic receptors coupled to the cAMP pathway modify the I(h) amplitude. Here, we show that direct activation of dopaminergic and of 5-HT receptors results in I(h) inhibition of SNc DA cells, whereas noradrenaline has the opposite effect. Together, these data suggest that the modulation of I(h) by endogenously released neurotransmitters acting on metabotropic receptors -mainly but not exclusively linked to the cAMP pathway- could contribute significantly to the control of SNc neuron excitability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
The h-current in periglomerular dopaminergic neurons of the mouse olfactory bulb.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56571. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056571. Epub 2013 Feb 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23418585 Free PMC article.
-
SK- and h-current contribute to the generation of theta-like resonance of rat substantia nigra pars compacta dopaminergic neurons at hyperpolarized membrane potentials.Brain Struct Funct. 2012 Apr;217(2):379-94. doi: 10.1007/s00429-011-0361-6. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Brain Struct Funct. 2012. PMID: 22108680
-
Effect of catecholamines on the hyperpolarization-activated cationic Ih and the inwardly rectifying potassium I(Kir) currents in the rat substantia nigra pars compacta.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Feb;11(2):398-406. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00452.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10051740
-
Activity-dependent regulation of the dopamine phenotype in substantia nigra neurons.J Neurochem. 2012 May;121(4):497-515. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2012.07703.x. Epub 2012 Mar 14. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22356203 Review.
-
Substantia nigra control of basal ganglia nuclei.J Neural Transm Suppl. 2009;(73):91-101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-211-92660-4_7. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2009. PMID: 20411770 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of HCN channels in the functions of basal ganglia and Parkinson's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Mar 13;81(1):135. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05163-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38478096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthetic mRNAs Drive Highly Efficient iPS Cell Differentiation to Dopaminergic Neurons.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019 Feb;8(2):112-123. doi: 10.1002/sctm.18-0036. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30387318 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic receptor activation preferentially inhibits rebound in vulnerable dopaminergic neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 31:2024.07.30.605819. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.30.605819. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 Apr 16;45(16):e1443242025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1443-24.2025. PMID: 39131326 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Enhanced Activation of HCN Channels Reduces Excitability and Spike-Timing Regularity in Maturing Vestibular Afferent Neurons.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 10;39(15):2860-2876. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1811-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30696730 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Quinine on Neurophysiological Properties of Dopaminergic Neurons.Neurotox Res. 2018 Jul;34(1):62-73. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9855-1. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 29285614
References
-
- Korotkova TM, Ponomarenko AA, Brown RE, Haas HL (2004) Functional diversity of ventral midbrain dopamine and GABAergic neurons. Mol Neurobiol 29: 243–259. - PubMed
-
- Labouebe G, Lomazzi M, Cruz HG, Creton C, Lujan R, et al. (2007) RGS2 modulates coupling between GABAB receptors and GIRK channels in dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area. Nat Neurosci 10: 1559–1568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

