Neutral fragment filtering for rapid identification of new diester-diterpenoid alkaloids in roots of Aconitum carmichaeli by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry
- PMID: 23285005
- PMCID: PMC3528760
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052352
Neutral fragment filtering for rapid identification of new diester-diterpenoid alkaloids in roots of Aconitum carmichaeli by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with linear ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry
Abstract
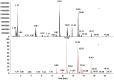
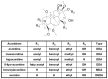
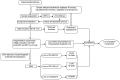
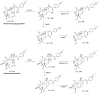
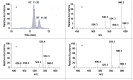
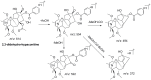
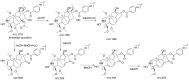
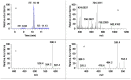
A rapid and effective method was developed for separation and identification of diester-diterpenoid alkaloids (DDA) in the roots of Aconitum carmichaeli by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution LTQ-Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS(n)). According to accurate mass measurement and the characteristic neutral loss filtering strategy, a total of 42 diester-diterpenoid alkaloids (DDA) were rapidly detected and characterized or tentatively identified. Meanwhile, the proposed fragmentation pathways and the major diagnostic fragment ions of aconitine, mesaconitine and hypaconitine were investigated to trace DDA derivatives in crude plant extracts. 23 potential new compounds were successfully screened and characterized in Aconitum carmichaeli, including 16 short chain fatty acyls DDA, 4 N-dealkyl DDA and several isomers of aconitine, mesaconitine and hypaconitine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid separation and characterization of diterpenoid alkaloids in processed roots of Aconitum carmichaeli using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with hybrid linear ion trap-Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry.J Sep Sci. 2014 Oct;37(20):2864-73. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201400365. Epub 2014 Sep 25. J Sep Sci. 2014. PMID: 25124198
-
Studies on the aconitine-type alkaloids in the roots of Aconitum Carmichaeli Debx. by HPLC/ESIMS/MS(n).Talanta. 2009 Mar 15;77(5):1800-7. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.10.022. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Talanta. 2009. PMID: 19159802
-
[Determination of three kind of diester diterpenoid alkaloids (DDAs) in Aconitum carmichaeli and its processed products by HPLC].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006 Jul;31(14):1160-2. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17048584 Chinese.
-
Aconitum lipo-alkaloids--semisynthetic products of the traditional medicine.Nat Prod Commun. 2011 Apr;6(4):527-36. Nat Prod Commun. 2011. PMID: 21560765 Review.
-
[Studies on structural elucidation of Aconitum diterpenoid alkaloid by LC-APCI-MS and effects of Aconitum diterpenoid alkaloid on cutaneous blood flow].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002 Nov;122(11):929-56. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.122.929. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12440151 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Use, history, and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry chemical analysis of Aconitum.J Food Drug Anal. 2016 Jan;24(1):29-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2015.09.001. Epub 2015 Oct 16. J Food Drug Anal. 2016. PMID: 28911407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Oxygenated Fatty Acid as a Side Chain of Lipo-Alkaloids in Aconitum carmichaelii by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS and a Database.Molecules. 2016 Mar 31;21(4):437. doi: 10.3390/molecules21040437. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27043515 Free PMC article.
-
Applying Four-Step Characteristic Ion Filtering with HPLC-Q-Exactive MS/MS Spectrometer Approach for Rapid Compound Structures Characterization and Major Representative Components Quantification in Modified Tabusen-2 Decoction.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 31;2021:9255305. doi: 10.1155/2021/9255305. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 35003312 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, synthesis and biological activity of alkyl-guanidine oligomers as potent antibacterial agents.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 15;7(1):8251. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-08749-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28811659 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Dynamic Changes of Chemical Constituents in Raw and Processed Fuzi With Different Steaming Time Points Using Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging Combined With Metabolomics.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 10;13:842890. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.842890. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35359875 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tai YT, But PP, Young K, Lau CR (1992) Cardiotoxicity after accidental herb-induced aconite poisoning. Lancet 340: 1254–1256. - PubMed
-
- Konno C, Shirasaka M, Hikino H (1979) Cardioactive Principle of Aconitum carmichaeli Roots. Planta Med 35: 150–155. - PubMed
-
- Lin CC, Chan TYK, Deng JF (2004) Clinical features and management of herb-induced aconitine poisoning. Ann Emerg Med 43: 574–579. - PubMed
-
- Chan TYK (2009) Aconite poisoning presenting as hypotension and bradycardia. Hum Exp Toxicol 28: 759–797. - PubMed
-
- Dickens P, Tai YT, But PP, Tomlinson B, Nge HK, et al. (1994) Fatal accidental aconitine poisoning following ingestion of Chinese herbal medicine: a report of two cases. Forensic Sci Int 67: 55–58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

