Methylene blue reduced abnormal tau accumulation in P301L tau transgenic mice
- PMID: 23285020
- PMCID: PMC3527507
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052389
Methylene blue reduced abnormal tau accumulation in P301L tau transgenic mice
Abstract
In neurodegenerative disorders, abnormally hyperphosphorylated and aggregated tau accumulates intracellularly, a mechanism which is thought to induce neuronal cell death. Methylene blue, a type of phenothiazine, has been reported to inhibit tau aggregation in vitro. However, the effect of methylene blue in vivo has remained unknown. Therefore, we examined whether methylene blue suppresses abnormal tau accumulation using P301L tau transgenic mice. At 8 to 11 months of age, these mice were orally administered methylene blue for 5 months. Subsequent results of Western blotting analysis revealed that this agent reduced detergent-insoluble phospho-tau. Methylene blue may have potential as a drug candidate for the treatment of tauopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
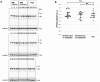
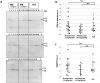
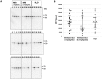
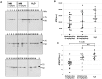
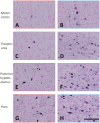
References
-
- Taniguchi S, Suzuki N, Masuda M, Hisanaga S, Iwatsubo T, et al. (2005) Inhibition of heparin-induced tau filament formation by phenothiazines, polyphenols, and porphyrins. J Biol Chem 280: 7614–7623. - PubMed
-
- Wischik CM, Bentham P, Wischik DJ, Seng KM (2008) Tau aggregation inhibitor (TAI) therapy with Rember arrests disease progression in mild and moderate Alzheimer's disease over 50 weeks. Alzheimer's & Dementia 8: T167.
-
- Gravitz L (2011) Drugs: a tangled web of targets. Nature 475: S9–11. - PubMed
-
- van Bebber F, Paquet D, Hruscha A, Schmid B, Haass C (2010) Methylene blue fails to inhibit Tau and polyglutamine protein dependent toxicity in zebrafish. Neurobiol Dis 39: 265–271. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

