An integrative approach to inferring gene regulatory module networks
- PMID: 23285197
- PMCID: PMC3527610
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052836
An integrative approach to inferring gene regulatory module networks
Abstract
Background: Gene regulatory networks (GRNs) provide insight into the mechanisms of differential gene expression at a system level. However, the methods for inference, functional analysis and visualization of gene regulatory modules and GRNs require the user to collect heterogeneous data from many sources using numerous bioinformatics tools. This makes the analysis expensive and time-consuming.
Results: In this work, the BiologicalNetworks application-the data integration and network based research environment-was extended with tools for inference and analysis of gene regulatory modules and networks. The backend database of the application integrates public data on gene expression, pathways, transcription factor binding sites, gene and protein sequences, and functional annotations. Thus, all data essential for the gene regulation analysis can be mined publicly. In addition, the user's data can either be integrated in the database and become public, or kept private within the application. The capabilities to analyze multiple gene expression experiments are also provided.
Conclusion: The generated modular networks, regulatory modules and binding sites can be visualized and further analyzed within this same application. The developed tools were applied to the mouse model of asthma and the OCT4 regulatory network in embryonic stem cells. Developed methods and data are available through the Java application from BiologicalNetworks program at http://www.biologicalnetworks.org.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

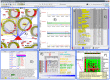
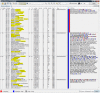

References
-
- Wilczynski B, Furlong EE (2010) Challenges for modeling global gene regulatory networks during development: insights from Drosophila. Dev Biol 340: 161–169. - PubMed
-
- Segal E, Shapira M, Regev A, Pe'er D, Botstein D, et al. (2003) Module networks: identifying regulatory modules and their condition-specific regulators from gene expression data. Nat Genet 34: 166–176. - PubMed
-
- De Smet R, Marchal K (2010) Advantages and limitations of current network inference methods. Nat Rev Microbiol 8: 717–729. - PubMed
-
- Bar-Joseph Z, Gerber GK, Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Yoo JY, et al. (2003) Computational discovery of gene modules and regulatory networks. Nat Biotechnol 21: 1337–1342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

