Integrin Beta 1 suppresses multilayering of a simple epithelium
- PMID: 23285215
- PMCID: PMC3528644
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052886
Integrin Beta 1 suppresses multilayering of a simple epithelium
Abstract
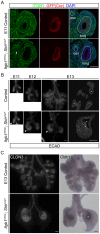
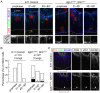
Epithelia are classified as either simple, a single cell layer thick, or stratified (multilayered). Stratified epithelia arise from simple epithelia during development, and transcription factor p63 functions as a key positive regulator of epidermal stratification. Here we show that deletion of integrin beta 1 (Itgb1) in the developing mouse airway epithelium abrogates airway branching and converts this monolayer epithelium into a multilayer epithelium with more than 10 extra layers. Mutant lung epithelial cells change mitotic spindle orientation to seed outer layers, and cells in different layers become molecularly and functionally distinct, hallmarks of normal stratification. However, mutant lung epithelial cells do not activate p63 and do not switch to the stratified keratin profile of epidermal cells. These data, together with previous data implicating Itgb1 in regulation of epidermal stratification, suggest that the simple-versus-stratified developmental decision may involve not only stratification inducers like p63 but suppressors like Itgb1 that prevent simple epithelia from inappropriately activating key steps in the stratification program.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Koster MI, Roop DR (2007) Mechanisms regulating epithelial stratification. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 23: 93–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

