Crystal structure of the human SUV39H1 chromodomain and its recognition of histone H3K9me2/3
- PMID: 23285239
- PMCID: PMC3532415
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052977
Crystal structure of the human SUV39H1 chromodomain and its recognition of histone H3K9me2/3
Abstract
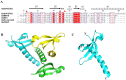
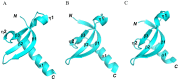
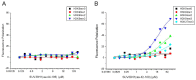
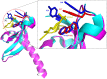
SUV39H1, the first identified histone lysine methyltransferase in human, is involved in chromatin modification and gene regulation. SUV39H1 contains a chromodomain in its N-terminus, which potentially plays a role in methyl-lysine recognition and SUV39H1 targeting. In this study, the structure of the chromodomain of human SUV39H1 was determined by X-ray crystallography. The SUV39H1 chromodomain displays a generally conserved structure fold compared with other solved chromodomains. However, different from other chromodomains, the SUV39H1 chromodomain possesses a much longer helix at its C-terminus. Furthermore, the SUV39H1 chromodomain was shown to recognize histone H3K9me2/3 specifically.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kouzarides T (2007) Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128: 693. - PubMed
-
- Volkel P, Angrand PO (2007) The control of histone lysine methylation in epigenetic regulation. Biochimie 89: 1–20. - PubMed
-
- Lachner M, O'Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001) Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410: 116–120. - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty S, Sinha KK, Senyuk V, Nucifora G (2003) SUV39H1 interacts with AML1 and abrogates AML1 transactivity. AML1 is methylated in vivo. Oncogene 22: 5229–5237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

