Extracellular ATP signaling is mediated by H₂O₂ and cytosolic Ca²⁺ in the salt response of Populus euphratica cells
- PMID: 23285259
- PMCID: PMC3532164
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053136
Extracellular ATP signaling is mediated by H₂O₂ and cytosolic Ca²⁺ in the salt response of Populus euphratica cells
Abstract
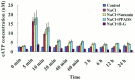
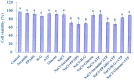
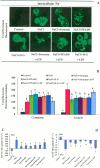
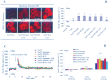
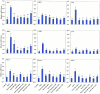
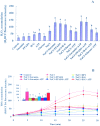
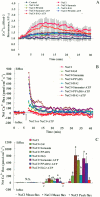
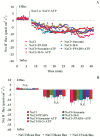
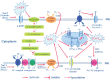
Extracellular ATP (eATP) has been implicated in mediating plant growth and antioxidant defense; however, it is largely unknown whether eATP might mediate salinity tolerance. We used confocal microscopy, a non-invasive vibrating ion-selective microelectrode, and quantitative real time PCR analysis to evaluate the physiological significance of eATP in the salt resistance of cell cultures derived from a salt-tolerant woody species, Populus euphratica. Application of NaCl (200 mM) shock induced a transient elevation in [eATP]. We investigated the effects of eATP by blocking P2 receptors with suramin and PPADS and applying an ATP trap system of hexokinase-glucose. We found that eATP regulated a wide range of cellular processes required for salt adaptation, including vacuolar Na⁺ compartmentation, Na⁺/H⁺ exchange across the plasma membrane (PM), K⁺ homeostasis, reactive oxygen species regulation, and salt-responsive expression of genes related to Na⁺/H⁺ homeostasis and PM repair. Furthermore, we found that the eATP signaling was mediated by H₂O₂ and cytosolic Ca²⁺ released in response to high salt in P. euphratica cells. We concluded that salt-induced eATP was sensed by purinoceptors in the PM, and this led to the induction of downstream signals, like H₂O₂ and cytosolic Ca²⁺, which are required for the up-regulation of genes linked to Na⁺/H⁺ homeostasis and PM repair. Consequently, the viability of P. euphratica cells was maintained during a prolonged period of salt stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zhang F, Wang Y, Yang YL, Wu H, Wang D, et al. (2007) Involvement of hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide in salt resistance in the calluses from Populus euphratica. . Plant Cell Environ 30: 775–785. - PubMed
-
- Tracy FE, Gilliham M, Dodd AN, Webb AAR, Tester M (2008) NaCl-induced changes in cytosolic free Ca2+ in Arabidopsis thaliana are heterogeneous and modified by external ionic composition. Plant Cell Environ 31: 1063–1073. - PubMed
-
- Sun J, Wang M, Ding M, Deng S, Liu M, et al. (2010) H2O2 and cytosolic Ca2+ signals triggered by the PM H+-coupled transport system mediate K+/Na+ homeostasis in NaCl-stressed Populus euphratica cells. Plant Cell Environ 33: 943–958. - PubMed
-
- Sun J, Li L, Liu M, Wang M, Ding M, et al. (2010) Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide mediate K+/Na+ homeostasis and antioxidant defense in NaCl-stressed callus cells of two contrasting poplars. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103: 205–215.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

