Clinical indications, advantages and limits of the expansion-condensing osteotomes technique for the creation of implant bed
- PMID: 23285355
- PMCID: PMC3415360
Clinical indications, advantages and limits of the expansion-condensing osteotomes technique for the creation of implant bed
Abstract
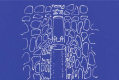
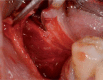
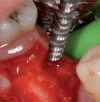
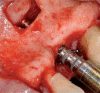
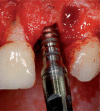
The "screw shaped" expansion-condenser are hand instruments that were introduced for the first time at the end of the 70' in order to improve bone density before the positioning of a dental implant. Thanks to these hand instruments it is possibile to compact the bone apically and along the walls of the implant bed (Fig. 3) improving a lot the bone density and the primary stability of the implant even in situations where the starting bone quality is low (es. D3-D4 as in the classification y Lekholm and Zarb 1985) or in cases of severe bone atrophy. Allowing a manageable raising of the shnaiderian membrane through trans-alveolar way, this technique avoids in many cases the necessity to have recourse to the realisation of bone vestibular "gates" when it comes to the techniques of the big sinus lift. The knoledge of the bone visco-elastic and hystologic properties together with the maximum respect of the surgical protocol allows us to obtein % of success superior than traditional surgical protocol in D3-D4 bone class.
Gli espanso-compattatori sono strumenti manuali introdotti per la prima volta alla fine degli anni ‘70 al fine di migliorare la densità ossea in vista del posizionamento di un impianto dentale. Grazie alla loro azione progressiva e costante all’interno delle compagini mascellari, sono in grado di compattare ed espandere le trabecole ossee migliorando la stabilità implantare primaria sia in situazioni iniziali di osso di scarsa qualità (es: D3-D4), sia in casi di atrofie severe. Permettono inoltre un maggior controllo durante la preparazione del letto implantare nei protocolli di piccolo e grande rialzo del seno mascellare. Di contro, questi strumenti, determinando un insulto alla micro-circolazione vasale per compressione trabecolare necessitano dello scrupoloso rispetto del protocollo operativo e della profonda conoscenza delle caratteristiche visco-elastiche dell’osso.
Keywords: bone condensing; oral implantology; ridge expansion.
Figures














References
-
- Tatum H. Maxillary and Sinus Implant Recostructions. Dent Clin North Am. 1986 - PubMed
-
- Osborn JF. Die Alveolar-Extensions Plastik. Quintessenz. 1985;36:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Scipioni A, Bruschi GB. The edentulous ridge expansion technique: a five year study. Int J Period Res Dent. 1994;14:451–459. - PubMed
-
- Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: the osteotome technique. Compendium of Contiunuing Education in Dentistry. 1994;15:152–158. - PubMed
-
- Simion M, Baldoni M, Zaffe D. Jawbone enlargement using immediate implant placement associated with a split crest technique and guided tissue regeneration. Int J Period Res Dent. 1992;12:462–473. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
