Striatal CB1 and D2 receptors regulate expression of each other, CRIP1A and δ opioid systems
- PMID: 23286559
- PMCID: PMC3697910
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.12139
Striatal CB1 and D2 receptors regulate expression of each other, CRIP1A and δ opioid systems
Abstract
Although biochemical and physiological evidence suggests a strong interaction between striatal CB1 cannabinoid (CB1 R) and D2 dopamine (D2 R) receptors, the mechanisms are poorly understood. We targeted medium spiny neurons of the indirect pathway using shRNA to knockdown either CB1 R or D2 R. Chronic reduction in either receptor resulted in deficits in gene and protein expression for the alternative receptor and concomitantly increased expression of the cannabinoid receptor interacting protein 1a (CRIP1a), suggesting a novel role for CRIP1a in dopaminergic systems. Both CB1 R and D2 R knockdown reduced striatal dopaminergic-stimulated [(35) S]GTPγS binding, and D2 R knockdown reduced pallidal WIN55212-2-stimulated [(35) S]GTPγS binding. Decreased D2 R and CB1 R activity was associated with decreased striatal phosphoERK. A decrease in mRNA for opioid peptide precursors pDYN and pENK accompanied knockdown of CB1 Rs or D2 Rs, and over-expression of CRIP1a. Down-regulation in opioid peptide mRNAs was followed in time by increased DOR1 but not MOR1 expression, leading to increased [D-Pen2, D-Pen5]-enkephalin-stimulated [(35) S]GTPγS binding in the striatum. We conclude that mechanisms intrinsic to striatal medium spiny neurons or extrinsic via the indirect pathway adjust for changes in CB1 R or D2 R levels by modifying the expression and signaling capabilities of the alternative receptor as well as CRIP1a and the DELTA opioid system.
© 2013 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
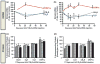


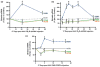

References
-
- Andersson M, Terasmaa A, Fuxe K, Stromberg I. Subchronic haloperidol increases CB(1) receptor binding and G protein coupling in discrete regions of the basal ganglia. J Neurosci Res. 2005;82:264–272. - PubMed
-
- Blazquez C, Chiarlone A, Sagredo O, et al. Loss of striatal type 1 cannabinoid receptors is a key pathogenic factor in Huntington’s disease. Brain. 2011;134:119–136. - PubMed
-
- Blume LC, Bass CE, Dalton GD, Selley DE, Howlett AC. Cannabinoid receptor interacting protein (CRIP) 1a: signal transduction and epigenetic phenomena. ICRS Symp Cannabinoids. 2010;20:P3–P30.
-
- Brady LS, Herkenham M, Rothman RB, Partilla JS, Konig M, Zimmer AM, Zimmer A. Region-specific up-regulation of opioid receptor binding in enkephalin knockout mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;68:193–197. - PubMed
-
- Cabral GA, Marciano-Cabral F. Cannabinoid receptors in microglia of the central nervous system: immune functional relevance. J Leukoc Biol. 2005;78:1192–1197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32-DA026295/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21-DA025321/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA006634/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01-DA024763/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA003690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA032215/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DA00724/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31-DA032215/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01-DA03690/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DA026295/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA025321/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA014030/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DA024763/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA006634/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030161/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

